- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Tetrazine Tango
Tetrazine Tango
💡 Can We Really Do More by Working Less?

Monday 21st July – Sunday 27th July 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 29 |


Mechanisms and Synthetic Applications of Cyclic, Nonstabilized Isodiazenes: Nitrogen-Atom Insertion into Pyrrolidines and Related Rearrangements
C. Elgindy, A. R. Gogoi, Á. Rentería-Gómez, B. Park, D. Das, C. E. Obertone, B. D. Dherange, O. Gutierrez* & M. D. Levin*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08361)
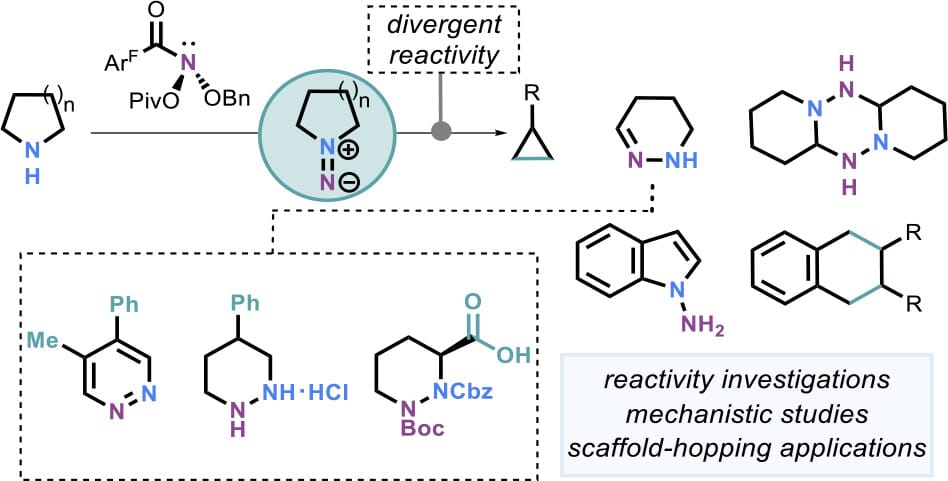
The authors study the reactivity of nonstabilized cyclic isodiazene intermediates generated via the reaction of cyclic secondary amines with an anomeric amide reagent. Depending on the amine structure, distinct product classes can be accessed, e.g. cyclic hydrazones are formed from pyrrolidines. Mechanistic experiments and DFT calculations suggest that many of these transformations proceed through an azomethine imine intermediate. In most cases, this species subsequently rearranges to a cyclic hydrazone by a self-catalysis mechanism proceeding through a dimeric tetrazine. This oxidative nitrogen insertion was leveraged in subsequent synthetic applications. Redox diversification of the cyclic hydrazones enabled access to pyridazines and cyclic hydrazines, including the synthesis of an orthogonally protected ʟ-piperazic acid from the readily available ʟ-prolinol.
👉️ For a recent, related publication by H. Lu and co-workers on the skeletal editing of pyrrolidines by nitrogen-atom insertion, see: here.

Catalytic C(sp2 ) Homologation of Alkylboranes
B. W. Gardner & G. Lalic*
Nat. Chem. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01854-4)
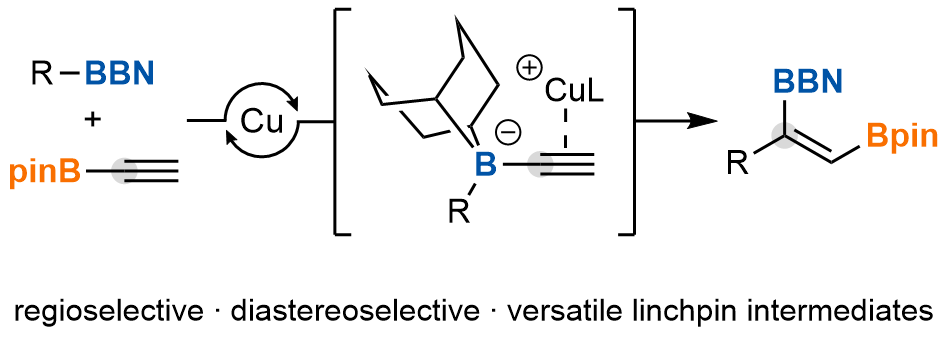
The authors report a catalytic C(sp2 )-insertive homologation for the regio- and diastereoselective synthesis of complex trisubstituted diborylalkenes from simple alkylboranes and alkynyl boronic esters. Broad reaction scope was demonstrated and the resulting products were applied to the modular and stereoselective synthesis of highly substituted alkenes.

C–H Amination of Arenes and Heteroarenes through a Dearomative (3+2) Cycloaddition
S. Pradhan, F. Mohammadi, R. Tanase, K. Amaike, K. Itami* & J. Bouffard*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c06390)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-mj889-v2) 🔓
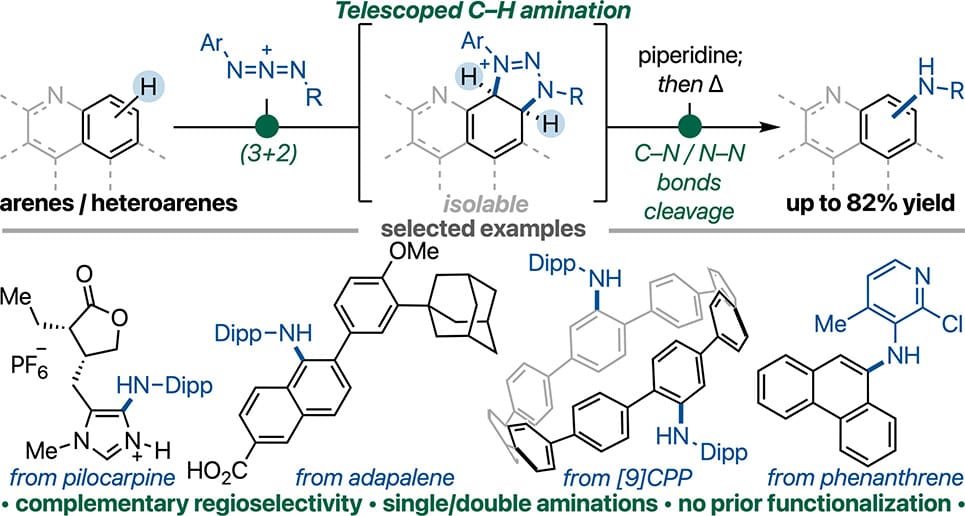
The authors report that azidium ions can enable the C–H amination of unactivated arenes and heteroarenes through a cycloaddition and C–N/N–N bond cleavage sequence. First, dearomative (3+2) cycloaddition reaction between aromatic substrates and azidium ions generated fused triazolinium adducts. Subsequent treatment with a mild base, followed by thermolysis, achieved the synthesis of a diverse range of arylamines. Comparison with electrophilic halogenation/Buchwald–Hartwig amination or Ir-catalyzed borylation/Chan–Lam amination sequences revealed that the new C–H amination can provide a regio- or site-selectivity that complements these widely used approaches.
Accelerated Discovery of Energy Transfer-Catalyzed Dearomative Cycloadditions through a Data-Driven Three-Layer Screening Strategy
D. Rana, C. Hümpel, R. Laskar, L. Schlosser, S. Korgitzsch, S. Dutta, C. G. Daniliuc & F. Glorius*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09249)
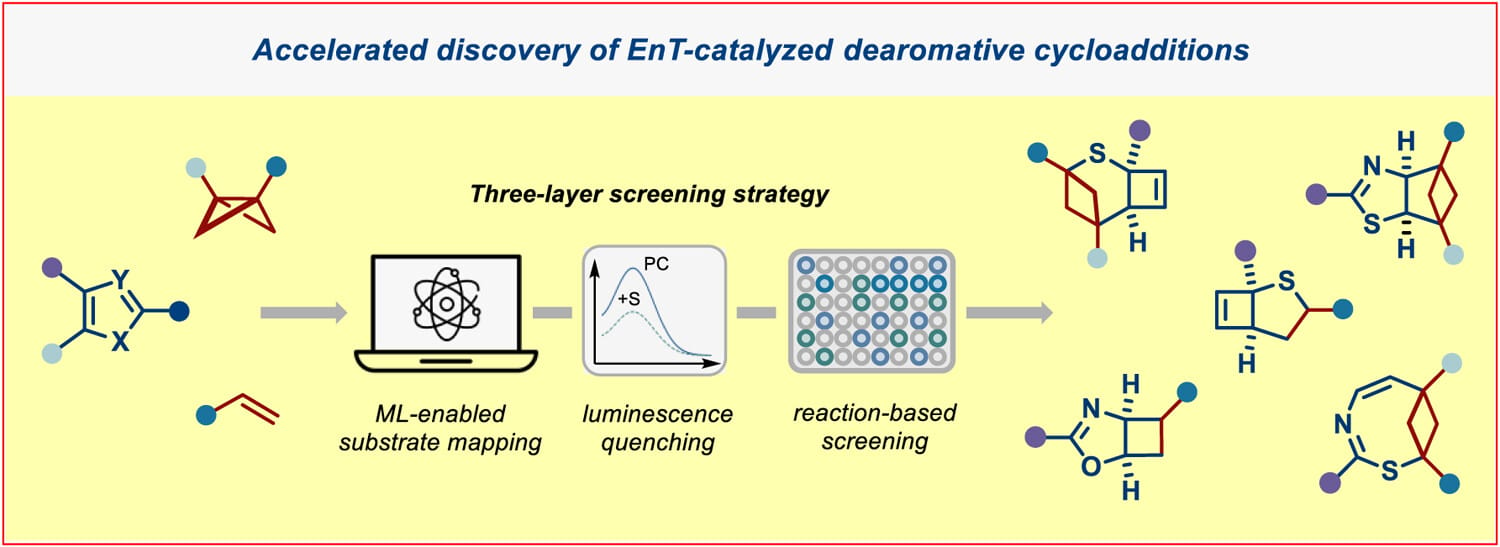
The authors report the energy transfer (EnT)-catalyzed intermolecular dearomative cycloaddition of monocyclic heteroarenes with alkenes and bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes. To overcome intrinsic limitations in triplet-state reactivity and accelerate reaction discovery, a data-driven three-layer screening strategy was introduced that integrates predictive data science tools for mapping excited-state properties with luminescence quenching and reaction-based screening. Utilizing this data-driven approach, the EnT-catalyzed intermolecular dearomative cycloaddition of thiophenes, oxazoles, and thiazoles with alkenes/bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes was developed.
Enantioselective Carbonylative Coupling Reactions: Merging Nickel-Based Selectivity and Photoredox Reactivity
L. Li, Z. Hu, S. Ren, B. A. Arndtsen* & L. Chu*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08527)
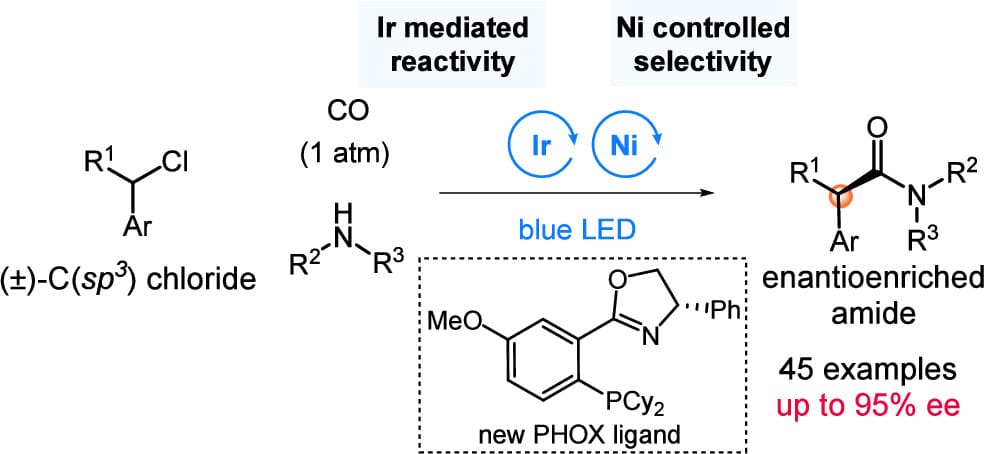
The development of enantioselective carbonylative coupling reactions of alkyl halides and nucleophiles to access α-chiral motifs is, to date, not viable. This has been attributed to the inhibitory influence of carbon monoxide, which blocks the activation of C(sp3 )-halides and limits the efficacy of chiral ligand environments in modulating selectivity. Here, the authors address this via a conceptually alternative approach, where the coupling of photoredox and chiral nickel catalysis can be employed to separate reactivity from stereocontrol. This strategy has enabled the first asymmetric carbonylative coupling of benzylic and related C(sp3 )-halides with amines and the preparation of a diverse array of chiral amides with excellent enantioselectivity.
Strain-Release-Driven Synthesis of Pentafluorosulfanylated Four-Membered Rings under Energy Transfer Photocatalysis
Y. Yang,† L. Han,† L. Canavero, L. Brettnacher, L. Khrouz, C. Monnereau, M. Médebielle & A. Tlili*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c07138)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-6z4c6) 🔓
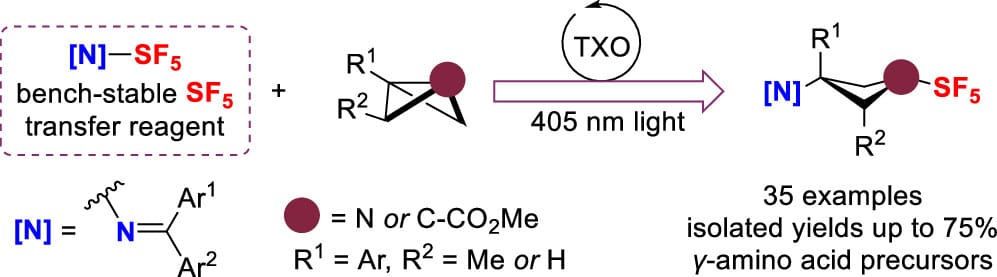
The pentafluorosulfanyl (SF5) group imparts unique chemical and physical properties, such as high electronegativity, and thermal stability, that are valuable in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. By using their shelf-stable reagent, imine-SF5, the authors enable selective access to four-membered ring SF5-containing molecules under mild reaction conditions via a strain-release approach facilitated by energy-transfer catalysis.
Direct N–SF5 and N–SF4CF3 Bond Formation through Strain-Release Functionalization of 3-Substituted [1.1.0]Azabicyclobutanes
Y. Kraemer,† S. Park,† W.-Y. Kong, Y. Chen, A. J. Witt, J. A. Buldt, A. N. Ragan, L. M. Holder, D. J. Tantillo* & C. R. Pitts*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c07137)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-68s1q) 🔓
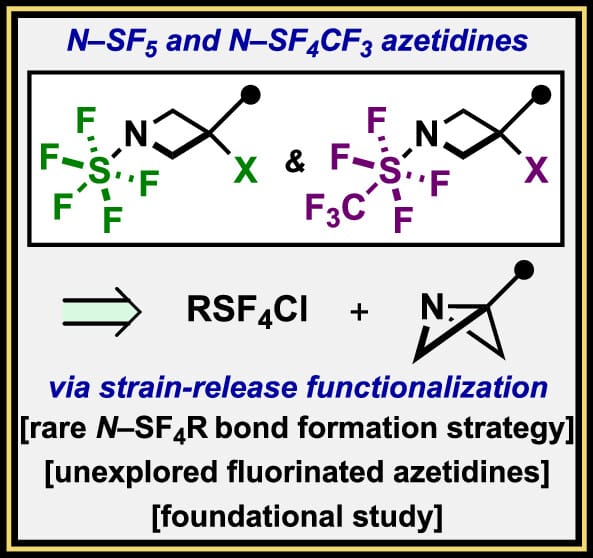
The authors demonstrate that N–SF5 bond formation can be accomplished through strain-release pentafluorosulfanylation of 3-aryl [1.1.0]azabicyclobutanes (ABBs), using an easy-to-access solution of SF5Cl. The resultant N–SF5 azetidines proved to be remarkably stable, amenable to peripheral synthetic modifications, and the methodology was capably extended to N–SF4CF3 bond formation using trans-CF3SF4Cl. The dynamic, spectroscopic, and crystallographic features of these azetidines were analyzed, as well as their computed properties. Finally, an N–SF5 derivative of a spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor was prepared for comparative ADME studies; results from in vitro profiling indicate that an N–SF5 azetidine could be an alternative for an N–SO2Me azetidine, in cases where enhanced lipophilicity is desirable.
Total Synthesis of Paxdaphnine A and Daphlongamine B via an Aza-Prins Cyclization Strategy
L. Ren,† Z. Lu,† D. Wu,† M. Ma & A. Li*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c04779)
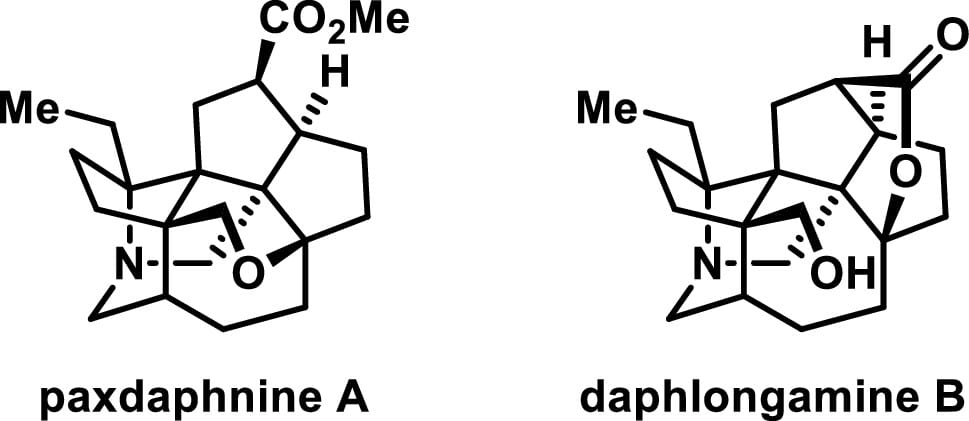
The authors report the first total syntheses of paxdaphnine A and daphlongamine B, two heptacyclic Daphniphyllum alkaloids with eight consecutive stereogenic centers, using a biomimetic aza-Prins cyclization strategy. Paxdaphnine B, a putative biogenetic precursor, was also obtained. A pentacyclic analogue of this was prepared in a scalable manner and served as a common intermediate.
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Bipolarolides A and B
Y. Liu,† K. Sun,† Q. Wei,† J. Chen, S. Sun, Y. Li, Z. Feng, Y. Guo & Z. Lu*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09835)
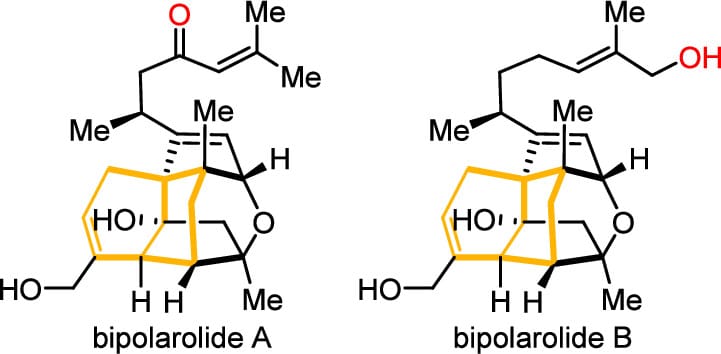
Bipolarolides A and B are members of the ophiobolin family of sesterterpenes, characterized by their intricate cage-like structures. Here, the authors report a concise asymmetric total synthesis of bipolarolides A and B enabled by the type-II Diels–Alder reaction. The synthesis features a sequence of key transformations: an iridium-catalyzed enantioselective allylation to establish the first stereocenter, type-II Diels–Alder reaction to rapidly assemble the bicyclo[3.3.1]non-1-ene core, reductive oxy-ring opening with olefin isomerization, aldol cyclization to construct a D ring, and a late-stage electrochemical C–H oxidation to complete the ether ring.
Scaffold Hopping of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones via Divergent Alkyl Amine Insertion
H. Yu, L. Xu, L. Li & C. Min*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c06690)
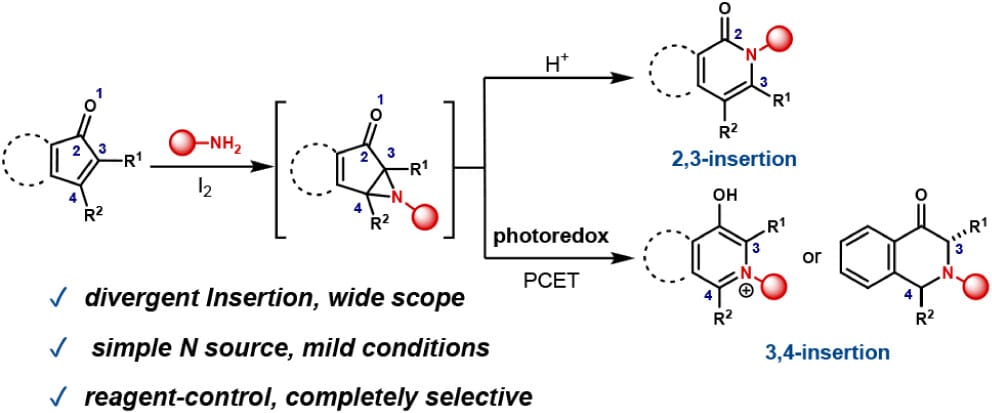
The authors report the divergent skeletal editing of α,β-unsaturated ketones via 2,3- and 3,4-amine insertion. The approach facilitates the selective incorporation of alkyl amines between C–C bonds within the same substrate. This reagent-controlled protocol enables tunable insertion sites through regioselective aziridine intermediate formation and targeted C–C bond cleavage, producing amine insertion products in a one-pot process.

Synthesis of Diaryl Ethers by Formal Oxygen Insertion Between Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling Partners
Y. Jiang, E. E. Kwan, Y. Ping & R. Y. Liu*
ACS Catal. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.5c03249)
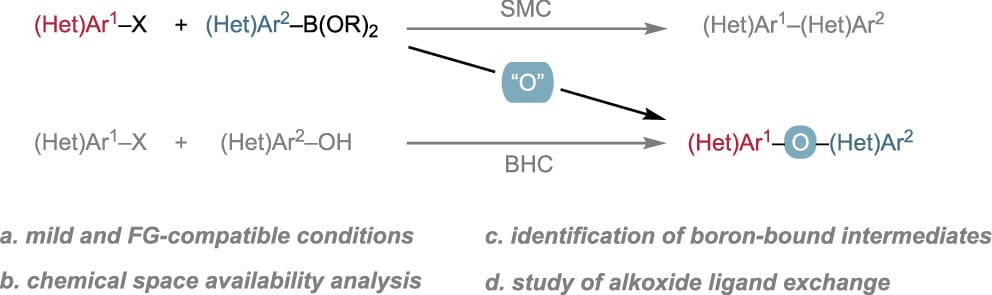
The authors report a three-component coupling strategy that formally inserts an oxygen atom into a Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling to yield diaryl ethers. The method is effective on aryl chlorides, tolerates a broad range of functional groups, and can be used when the corresponding (hetero)aryl alcohol is less accessible (unavailable, unstable, or not easily synthesized).

Synthesis of Thiophenes from Pyridines using Elemental Sulfur
Z. Liu & M. F. Greaney*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202512321) 🔓
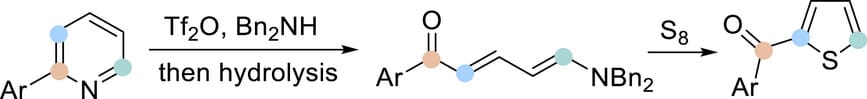
The authors describe a skeletal editing of pyridines to afford thiophenes through a formal [4+1] reaction using elemental sulfur. 2-Arylpyridines are converted to ring-opened aza-triene Zincke ketone structures, followed by simple treatment with sulfur to give 2-aroylthiophene products under mild conditions. This new transformation was exemplified in the synthesis of the anti-inflammatory drug suprofen from a pyridine starting material.
Total Synthesis and Structure Determination of Mycapolyol E Using Iterative Homologation of Boronic Esters
S. G. Aiken,† D. Rigby,† D. Fiorito, M. R. P. George, S. Wübbolt, A. Noble & V. K. Aggarwal*
Angew. Chem. Novit 2025, 1, e70003 (DOI: 10.1002/anov.70003) 🔓
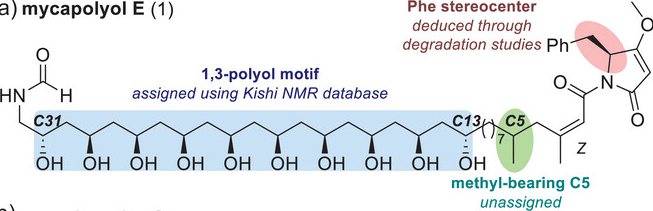
Mycapolyol E is a cytotoxic polyketide synthase/nonribosomal peptide synthetase (PKS/NRPS) metabolite isolated from a marine sponge containing an extended polyacetate motif, terminal formamide moiety, and tetramic acid-derived headgroup, whose structure could not be fully elucidated upon isolation. A modular approach was employed and the ten 1,3-related hydroxy-substituted stereocenters were installed through iterative diboration/homologation reactions. Furthermore, the stereochemistry of the unassigned methyl stereocenter at C5 was elucidated through partial synthesis and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, and the uncertainty surrounding the relative stereochemistry of the 1,3-polyol was resolved. The stereochemistry and structure of mycapolyol E was confirmed through total synthesis, which was completed in 20 steps longest linear sequence (LLS).
👉️ First highlighted publication from Angewandte Chemie’s new Gold Open Access journal, Angewandte Chemie Novit.

Unified Total Synthesis of Phrymarolin and Haedoxan Natural Products
J. Paciorek, A. D. F. Guy, A. Sudau, D. M. Barber & T. Magauer*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-t4s4h) 🔓
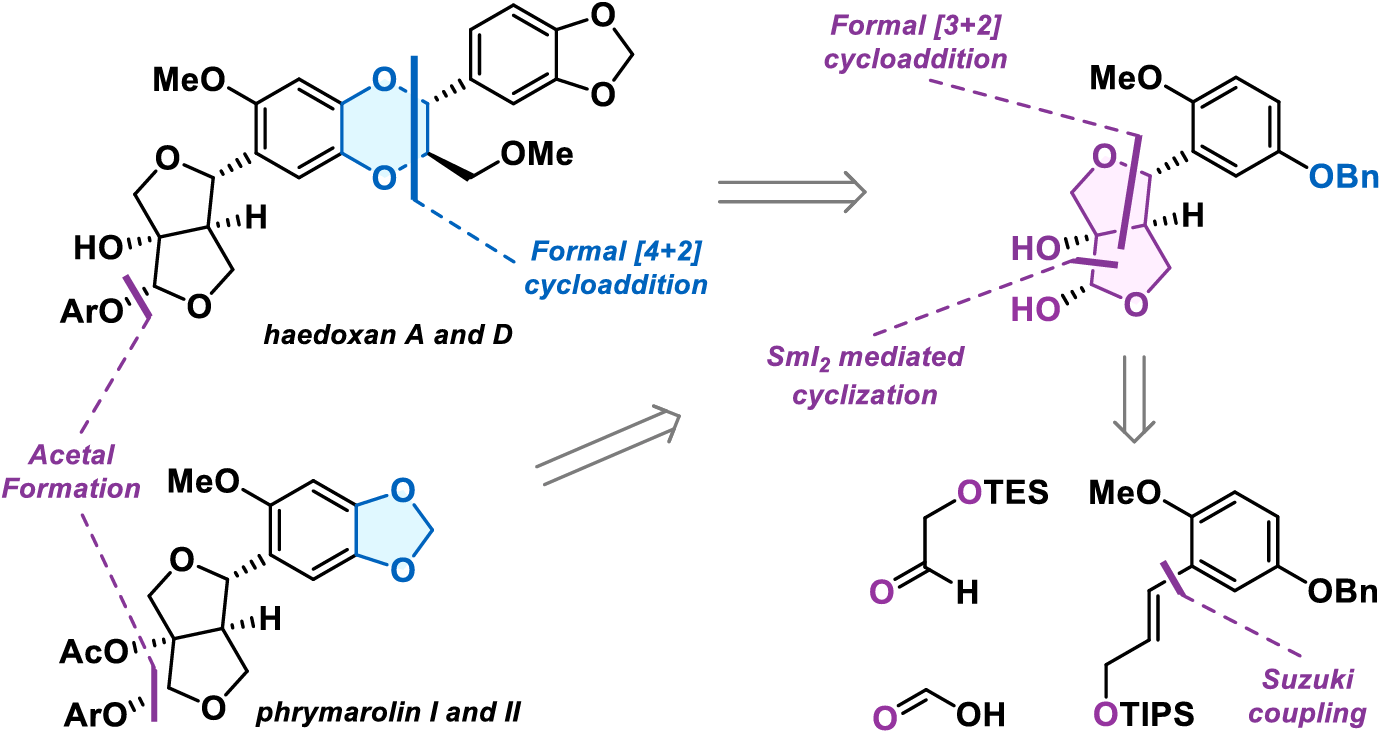
The authors disclose a unified synthetic route to the furofuran lignans phrymarolin I and II as well as the insecticidal natural products haedoxan A and D. The furofuran core was constructed using a formal [3+2] cycloaddition followed by a samarium(II) iodide promoted-cyclization. While this enabled the synthesis of phrymarolin I and II in eight steps, attempts to unmask the ortho-quinone necessary for a bioinspired formal [4+2] cycloaddition were unsuccessful, preventing access to the haedoxans. However, revising the arene substitution pattern enabled formation of the requisite ortho-quinone and facilitated a bioinspired cyclization to the 1,4-benzodioxane motif. Finally, late-stage diversification of the acetal completed the synthesis of haedoxan A and D in thirteen steps.
Flow-Enabled, Modular Access to α,α-Difluoromethylene Amines
D. Nagornîi, P. Ronco, K. Anwar, N. Kaplaneris, J. J. Douglas & T. Noël*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-z4lnw) 🔓
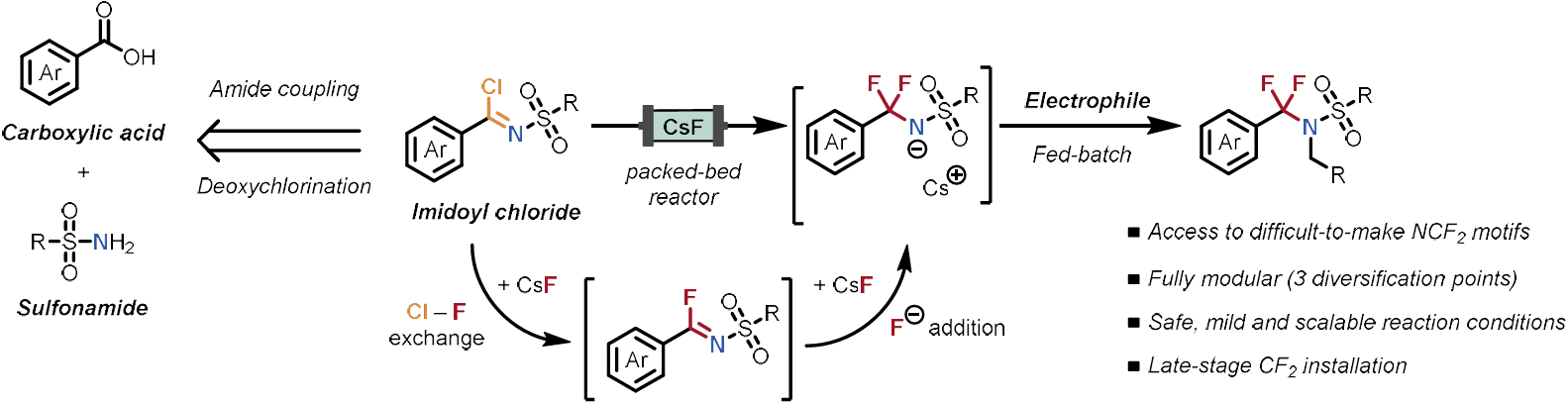
The authors report a safe and scalable flow-based strategy for the on-demand generation of α,α-difluoromethylene amine (NCF2R) anions using a packed-bed microreactor containing caesium fluoride. The protocol enables the late-stage installation of the CF2 group under mild conditions, avoiding the use of hazardous fluorinating agents and minimizing fluorinated waste. This fully modular strategy features three points of diversification (carboxylic acid, sulfonamide, and electrophile), allowing efficient access to a broad range of α,α-difluoromethylene amines.

Combining Biocatalytic and Radical Retrosynthesis for Efficient Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Natural Products
H. Renata*
Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, Advance Article (DOI: 10.1039/D5CS00453E) 🔓
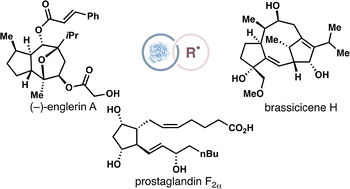
Retrosynthetic strategies are intimately tied to the tools and methods available at the time of their conception. Recent methodological advancements in both radical and biocatalytic reactions have created numerous possibilities for new and unconventional disconnections. Thus, it comes as no surprise that their applications in multi-step syntheses have allowed many complex molecules to be built in ingenious ways. This review summarizes recent case studies wherein radical-based and enzymatic transformations are combined strategically in multi-step sequences to achieve efficient total syntheses of complex natural products.

What If Friday Was Always Off?
🍃 What If Friday Was Always Off? In 1930, economist John Maynard Keynes predicted that by 2030, technological advancements and increased productivity would significantly shorten the working week, possibly to just 15-hours. Fast forward to 2007, and author Tim Ferriss went even further with his 4-Hour Workweek. Yet here we are, now five years away from 2030, still clocking in at more than double Keynes’ optimistic forecast.
Now, a six-month trial spanning six countries (Australia, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand, the UK, and the USA) has found that switching to a four-day work week—without reducing pay, of course—can lead to happier, healthier, and more productive employees. Nearly 3,000 employees across 141 companies took part, with businesses restructuring workflows to deliver the same output in 80% of the time by cutting out inefficiencies (like those meetings that really should’ve been an email).
The results? Burnout dropped, job satisfaction rose, and both mental and physical health improved. Despite initial concerns, stress levels actually decreased. Crucially, over 90% of participating companies chose to stick with the shorter week after the trial ended, suggesting productivity and profits held steady.
While outcomes were self-reported and the trial was voluntary, potentially skewing results, the findings add weight to the case for a shorter working week. The researchers are now calling for randomized studies to confirm the impact at scale.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply