- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Targeting (+)-Talaromyolide D
Targeting (+)-Talaromyolide D
💡 Journal Rankings for 2025: Organic Chemistry’s New “Number One” Might Surprise You

Monday 11th August – Sunday 17th August 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 32 |


Total Synthesis of the Nominal Structure of (+)-Talaromyolide D
B. Qin, A. Szyperek & M. Tomanik*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c10325) 🔓

The authors report a total synthesis of the nominal structure of (+)-talaromyolide D, a meroterpenoid possessing a unique pentacyclic skeleton distinguished by a fused 6/6/6 dihydroisocoumarin core and an unusual pendant dimethylcyclobutanol. The synthetic strategy was enabled by a stereoretentive, nickel-catalyzed electrochemical sp2 –sp3 decarboxylative cross-coupling, a two-fold bidirectional stitching sequence comprised of an oxime-directed β-C(sp3 )–H arylation and SNAr to establish the central ring system as well as a series of late-stage carboxylic-acid-directed C(sp2 )–H oxidation reactions to access the isocoumarin lactone substructure. However, comparison of the spectral data showed that the structure of this natural product had been misassigned.

Enantioconvergent Benzylic C(sp3 )‒N Coupling with a Copper-Substituted Nonheme Enzyme
X. Shen, X. Chen, Y. Xiao, J. B. Brown, J. G. Zhang, X. Ji, J. Rui, M. Garcia-Borràs, Y. Rao*, Y. Yang* & X. Huang*
Science 2025, 389, 741–746 (DOI: 10.1126/science.adt5986)

The authors introduce a photobiocatalytic approach for radical benzylic C(sp3 )‒N coupling using a copper-substituted nonheme enzyme. Using rhodamine B as a photoredox catalyst, a copper-substituted phenylalanine hydroxylase was identified that facilitates enantioconvergent decarboxylative amination between N-hydroxyphthalimide esters and anilines. Directed evolution remodeled the active site, resulting in high enantioselectivities for most substrates.

Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Alkylidenecyclopropanes
J. C. Golec,† D.-H. Tan,† K. Yamazaki, E. H. Tiekink, K. E. Christensen, T. A. Hamlin* & D. J. Dixon*
Nature 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09485-y)

The authors describe the synthesis of highly enantioenriched alkylidenecyclopropanes through the use of a bifunctional iminophosphorane (BIMP) catalysed, stereo-controlled, strain-relieving deconjugation. Small modifications to the catalyst system were used to broaden the scope of the reaction to substrates containing ester, amide, phosphine oxide, and ketone functionalities. Through the design of a suitable substrate and re-tuning of the catalyst’s iminophosphorane moiety, the transformation was effectively applied to the synthesis of a single stereoisomer of the commonplace insecticide permethrin as well as a range of cyclopropane-based insecticide cores.

A Broadly Applicable Stereospecific Glycosylation
Q. Zhang, N. J. Flodén, Y. Zhang, J. Yang, P. Kohnke, J. Danglad-Flores, E. T. Sletten, P. H. Seeberger* & L. Zhang*
Nat. Synth. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00846-z)

The authors disclose a stereospecific glycosylation method that accommodates a broad range of monosaccharides, including hexopyranoses (glucose, galactose, mannose, fucose, alluronate, 2-azido-2-deoxyglucose and 2-azido-2-deoxygalactose) and pentofuranoses (arabinose, ribose, xylose and lyxose). Mild activation with an electrophilic bromine reagent results in complete inversion of the anomeric configuration and excellent yields for many glycosylations. The method proved reliable in multistep oligosaccharide syntheses and automated glycan assembly.

Photochemical Permutation of meta-Substituted Phenols
M. Alonso,† G. Lonardi,† E. M. Arpa, B. Roure, A. Ruffoni* & D. Leonori*
Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7502 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62549-5) 🔓

The authors report an alternative approach for phenol synthesis where irradiation in the presence of Lewis or Brønsted acids enables the selective migration of alkyl and aryl groups from meta- to either the ortho- or para-positions. By leveraging selective photoexcitation, precise control over the directionality of the permutation process can be achieved. Specifically, short-wavelength irradiation (λ = 310 nm) promotes meta→para migration, while longer-wavelength irradiation (λ = 390 nm) meta→ortho. The applicability of the method has been demonstrated on the isomerization of poly-substituted derivatives including some bioactive species.

Total Synthesis of (±)-Crokonoid A
T. Martini, N. Saab, J. Muschietti & E. M. Carreira*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c11026)
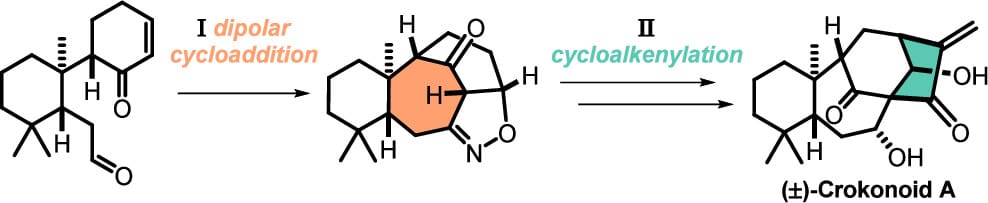
The authors report the first total synthesis of (±)-crokonoid A, a highly oxidized and rearranged ent-kauranoid featuring a novel tricyclo[4.4.1.11,4 ]dodecane scaffold. The unique double bridged carbon skeleton was assembled by synthesis of the bicyclo[4.3.1]decane via nitrile-oxide dipolar cycloaddition. Salient features of this strategy are the construction of the bridged system and masking the twofold aldol motif as an isoxazoline. An unconventional bridgehead propargylation set the key quaternary stereocenter concomitant with side chain installation. Subsequent cycloalkenylation led to construction of the bicyclo[3.2.1]octane, completing the carboskeleton.
A Data Science-Guided Approach for the Development of Nickel-Catalyzed Homo-Diels–Alder Reactions
J. A. Cadge,† C. Lozano,† M. T. Merriman, P. Oblad, M. S. Sigman* & S. E. Reisman*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09948)

The Ni-catalyzed homo-Diels–Alder (hDA) reaction represents a convergent but under-investigated approach to preparing bridged bicyclic ring systems. Using the kraken monophosphine descriptor library, Ni-catalyzed hDA reactions of acyclic and cyclic electron deficient olefins were investigated, and key ligand effects required for reactivity were identified using classification models. The resultant cycloadducts were transformed into bicycloheptane structures via cyclopropane cleavage reactions.
Direct Synthesis of Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes by Sequential C=C, C–C Functionalization Reactions
J. K. Sailer,† D. Ly,† D. G. Musaev & H. M. L. Davies*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09039) 🔓

2-Substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane carboxylates have been synthesized using two sequential carbene reactions. A dirhodium-catalyzed intramolecular cyclopropanation to form a bicyclo[1.1.0]butane is followed by a photoinduced formation of a triplet carbene, which undergoes a diradical addition into the strained C–C bond of the bicyclo[1.1.0]butane. A variety of novel 2-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes have been synthesized in good to moderate yields, offering rapid access to these valuable scaffolds.
Photochemical Insights on Acyl Azolium Salts Enable the Design of a Tandem Hydrogen Atom Transfer/Halogen Atom Transfer Acylation of Alkyl Bromides and Chlorides
I. MacLean, D. J. Grenda, E. Echávarri, S. Muth, P. Nuernberger & L. Marzo*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c10923) 🔓

The authors present a photochemical study of the reactivity of acyl azolium salts that comprises the detection and characterization of the triplet excited state and the decisive ketyl radical intermediate. This mechanistic insight facilitated the development of an alternative method based on a silane-mediated tandem HAT/XAT activation strategy that enables not only the acylation of alkyl bromides but also more challenging alkyl chlorides. Furthermore, its robustness has been proven through the functionalization of natural product derivatives either as acyl azolium or alkyl bromide derivatives.

Deoxygenative Functionalization of Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds via Electrochemical Reduction
A. J. Ressler, J. I. M. Alvarado, R. Hariharan, W. Guan & S. Lin*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Accepted (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202510069)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-0dfb4) 🔓

Oxygen-containing functional groups are prevalent in natural products and feedstock chemicals, but direct methods for their deoxygenative transformation remain rare due to difficulties in cleaving the strong C–O bond. Here, the authors report a general activation strategy that employs hydrosilanes as activating reagents for alcohols, carbonyls, and esters to afford a common silyl ether intermediate. Electrochemical reduction of the in situ generated silyl ether results in C–O cleavage to afford a carbanion, which reacts with a number of electrophiles for the construction of C–Si, C–B, C–Ge, and C–Sn bonds.

Regiodivergent Cation Sampling for Distal Csp3 -Functionalization
P. Spieß,† M. Vavrík,† J. Frey, U. Vezonik, D. Kaiser & N. Maulide*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-ks4x0) 🔓

The authors report a cationic olefin isomerization process for regiodivergent Csp3 –H functionalization, wherein the selectivity results from a ketone-assisted process termed “cation sampling”. This method enables site-selective, on-demand regiodivergent functionalization of Csp3 carbons, allowing the formation of C–heteroatom bonds in challenging positions and unlocking access to products that were previously unattainable through metal-based methodologies. The platform is not limited to olefinic substrates, also offering a versatile framework for alcohol transposition reactions, a formal migratory Appel reaction, and an effective solution for resolving regioisomeric bromohydrin mixtures.
Facile Aryl C–N Bond Formation via SNAr Using Photothermal Red Light Activation
M. E. Matter,† R. C. Devin† & E. E. Stache*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-st87c) 🔓

The authors demonstrate that an inexpensive photothermal agent, carbon black, and irradiation with red light enables aryl C–N bond formation via nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr). Electron neutral, intramolecular analogs were also amenable to the process in short time frames (3–20 minutes) and the approach was further leveraged into a one pot, two step SNAr, where an initial intermolecular reaction occurs followed by a second, intramolecular substitution, allowing for the formation of a diverse scope of fused heterocycles.
👉️ For an additional, recent publication by the Stache group on “Direct Aryne Generation from Aryl Halides via Photothermal Red-Light Activation”, see: here.
Fragmentation of Cyclic Oximes to Alkynes Enabled by Anomeric Amides
M. Ociepa* & D. Chauhan
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-j62lz) 🔓

The authors expand the reactivity of nitrenium ion precursors through the development of an unprecedented reaction between anomeric amides and cyclic oximes, namely, isoxazol-5-ones. This transformation provides an operationally simple, scalable, and highly chemoselective route to challenging sterically hindered alkynes.

Alkene Oxyamination: One-Pot Synthesis of Unprotected N–H Amino γ-Lactones
A. M. R. Treviño, Y.-D. Kwon & L. Kürti*
Org. Lett. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c02820)

The authors report a mild, Rh-catalyzed alkene oxyamination protocol for the synthesis of N–H unprotected amino γ-lactones. This method enables efficient coupling of a broad range of alkenyl carboxylic acids with structurally complex, O-activated hydroxylamines. The utility of the transformation is further demonstrated through the late-stage functionalization of active pharmaceutical ingredients.

Reimagining Advanced Chemistry Education: A Community-based Approach to Course Design for Modern Learners
M. A. Horwitz,* R. Al-Ahmad, X. Bai, M. Balletti, P. Bellotti, Y. Ben-Tal, M. W. Campbell, K. Cheasty, S. W. M. Crossley, C. S. Day, P. J. Deneny, K. C. Forbes, E. S. Gogarnoiu, P. S. Grant, R. Halder, G. R. Harris, P. Hernández-Lladó, M. Jouanneau, V. Jost, D. A. Kutateladze, G. Laudadio, C. Liu, A. P. Looby, A. Maestro, T. McCallum, M. D. Palkowitz, J. M. Paolillo, M. W. D. Perry, J. C. Reisenbauer, C. Reyes, H. A. Sharma, F. K. Sheong, B. Thoma, A. V. Tran, D. N. Tran, F. J. A. Troyano, T. Verheyen, M. P. Walsh, A. Wagner, E. R. Wearing & G. Wuitschik
J. Chem. Educ. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.5c00555)

The authors report the development of an open access Advanced Organic Chemistry video-based online course and several other specialized minicourses using the Synthesis Workshop YouTube channel with the goal of producing widely accessible graduate-level learning content and a community-based approach to online course design that is easily digestible.

Gaming The System
📈 Gaming the system. If you had to pick the most impactful journal in organic chemistry for 2025, what would it be…?
Well, according to Clarivate (owner of Web of Science), the correct answer is Carbohydrate Polymers. Yes, you read that right. Clarivate have recently published their latest Top 5 chemistry journals across multiple subfields, ranked by Journal Impact Factor (JIF) and Journal Citation Indicator (JCI)—metrics that attempt to capture journal impact via citation data—it’s not all doom and gloom though, at least Organic Letters came in at number 4.
JIFs have long been criticised for being gameable, inflated, and biased toward journals heavy on “front matter” (news and editorials) rather than primary research. Whereas JCI aims to normalise citation metrics between fields. An admirable goal but clearly not without its challenges.
If you’re curious about the other disciplines: Chinese Journal of Catalysis topped Applied Chemistry, Coordination Chemistry Reviews led Inorganic, and Nature Catalysis claimed Physical Chemistry, for some reason. Meanwhile, the Medicinal Chemistry rankings are no less surprising: Chinese Herbal Medicines and Phytomedicine make the top 5, while staples like J. Med. Chem. are nowhere to be seen. For a great write-up of these new “rankings”, see Derek Lowe’s aptly titled “Journal Impact Nonsense”.
What do you think? Perhaps we should be highlighting more Carbohydrate Polymers and less Journal of the American Chemical Society…
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply