- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Synthesis vs. Superbugs
Synthesis vs. Superbugs
💡 From Peasants to Princes: The Power of Progress

Monday 13th October – Sunday 19th October 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 39 |


The Total Synthesis of (−)-Spiroaspertrione A: A Divinylcyclopropane Rearrangement Approach
W. Huang,† L. Pan,† H. Zhao, F. Schneider* & T. Gaich*
Science 2025, 390, 261–265 (DOI: 10.1126/science.adz7593)
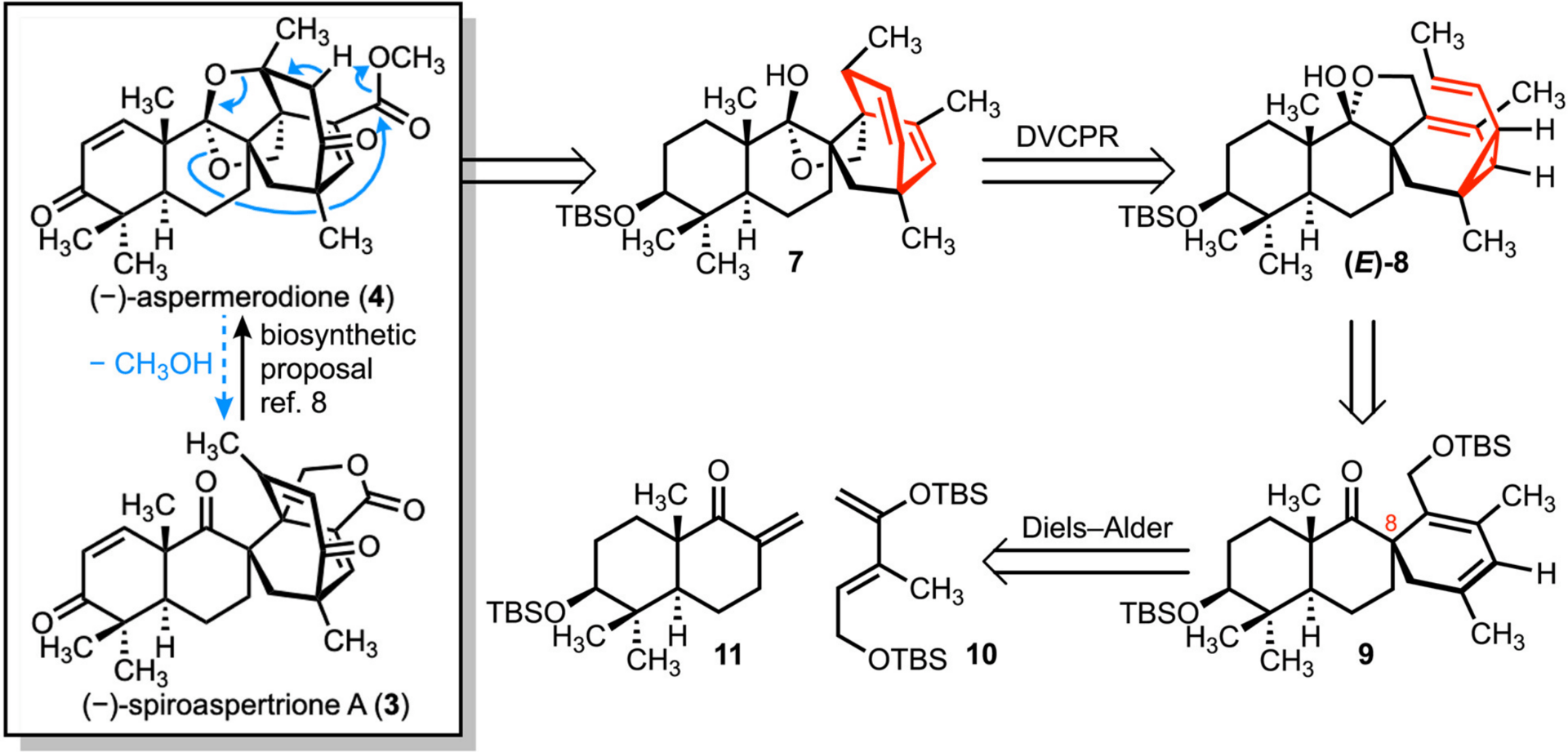
The rise of multidrug-resistant pathogens poses a major threat to global health, with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) among the most challenging. One promising approach to overcoming resistance is using small molecules that resensitize MRSA to existing drugs. Here, the authors report the enantioselective total synthesis of one such promising candidate, (−)-spiroaspertrione A, a complex meroterpenoid of the andiconin family. The route features a stereoselective Diels-Alder cycloaddition, followed by a key divinylcyclopropane rearrangement forming the spirobicyclo[3.2.2]nonane core. Strategic late-stage functionalization of the compact cage architecture enabled access to the natural product and provided evidence for a plausible biosynthetic relationship with (−)-aspermerodione.

Visible Light-Driven Stereodivergent Allylation of Cyclic Hemiacetals with Butene for Polypropionate Synthesis
H. Nakao,† M. M. M. Hassan,† Y. Nakamura, M. Toyobe, M. Higashi, H. Mitsunuma* & M. Kanai*
Science 2025, 390, 272–278 (DOI: 10.1126/science.adz0686)

The authors authors report a catalytic stereodivergent allylation of unprotected cyclic hemiacetal aldols with butene, enabling the programmable synthesis of polypropionates—privileged structural motifs prevalent in biologically active compounds, including pharmaceuticals. This visible light–driven, selective transformation exhibits broad functional group compatibility, furnishing 1,3-polyols with multiple contiguous stereocenters in high yield and stereochemical fidelity.

Deaminative Cross-Coupling of Amines by Boryl Radical β-Scission
Z. Zhang,† G. Lonardi,† T. Sephton,† Y. C. Guersoy, C. Stavagna, G. V. A. Lenardon, M. Bietti & D. Leonori*
Nature 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09725-1)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-ch3wj) 🔓

The authors report a strategy that repositions native primary, secondary, and tertiary amines as handles for cross-coupling. The platform relies on in situ activation via borane coordination and exploits a copper catalytic redox system that generates amine-ligated boryl radicals, which undergo β-scission across the C(sp3 )–N bond to release alkyl radicals. These intermediates engage in copper-catalyzed cross-couplings with a broad array of C-, N-, O-, and S-based nucleophiles. The method tolerates diverse amine classes, enables modular functionalization, and supports late-stage editing of complex drug scaffolds.
Photocatalytic Oxygen-Atom Transmutation of Oxetanes
Y.-Q. Zhang,† S.-H. Li,† X. Zhang* & M. J. Koh*
Nature 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09723-3)
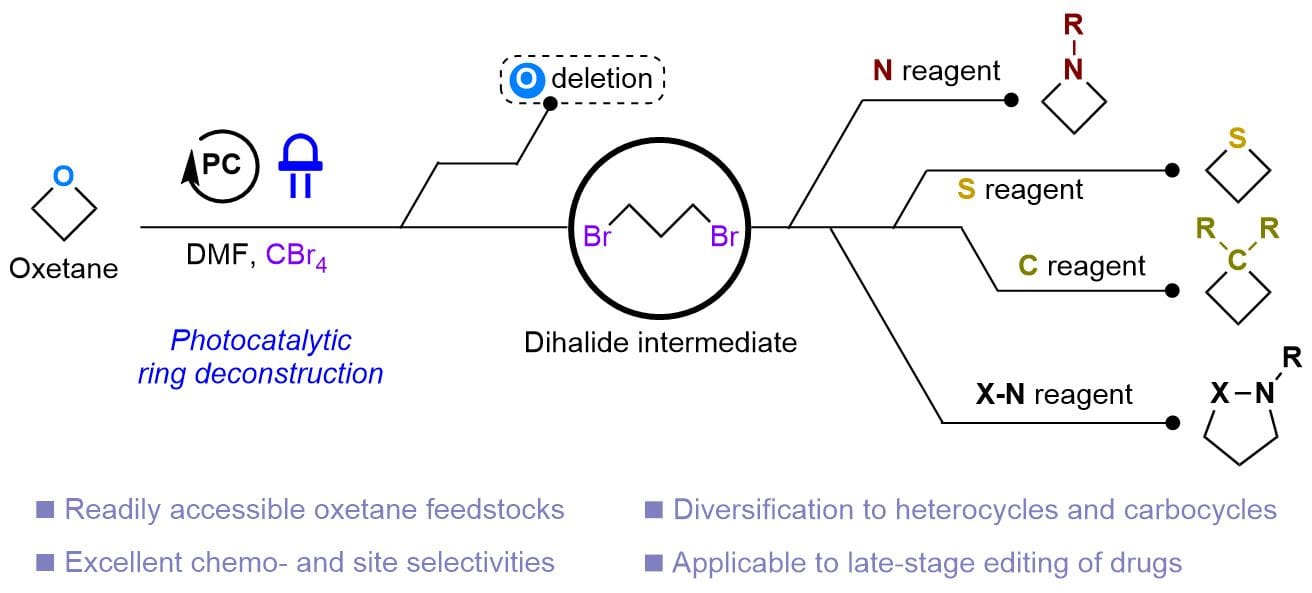
The authors report a general photocatalytic strategy that selectively substitutes the oxygen atom of an oxetane with a nitrogen-, sulfur- or carbon-based moiety, transforming it into a diverse range of saturated cyclic building blocks in a single operation. This atom swapping method exhibits high functional group compatibility and is applicable to late-stage functionalization, substantially simplifying the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and complex drug analogues that would otherwise require multi-step routes.

Overcoming Limitations in Chan-Lam Amination with Alkylboronic Esters via Aminyl Radical Substitution
H. Xiao, P. Cao, W. Xiong & T. Yang*
Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 9121 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-64155-x) 🔓
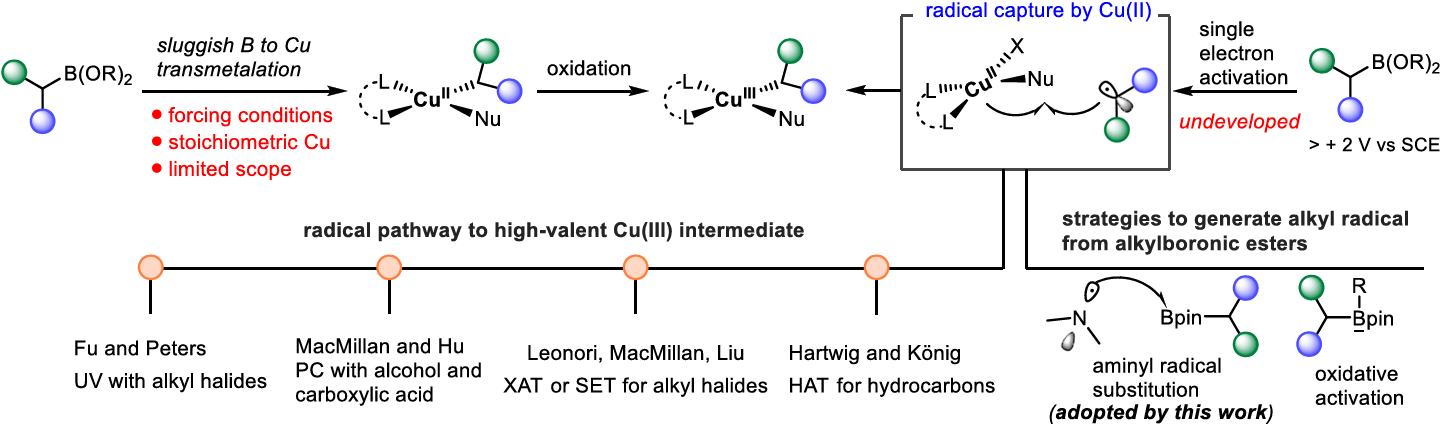
The authors report an N-alkylation protocol that overcomes the limitations of Chan-Lam coupling by using versatile alkylboronic pinacol esters as radical precursors via aminyl radical-mediated boron abstraction. This approach enables a versatile N-alkylation applicable to a range of alkylboronic pinacol esters and N-nucleophiles with diverse functional groups. Synthetic utility of this protocol is demonstrated by its ease of scalability and the late-stage modification of complex bioactive materials.

Development of a Ligand for Cu-Catalyzed Amination of Base-Sensitive (Hetero)aryl Chlorides
H.-J. Ai, B. K. Mai, C. Liu, P. Liu* & S. L. Buchwald*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c10910)

The authors report a new N1 ,N2 -diarylbenzene-1,2-diamine ligand that supports a copper catalyst capable of coupling base-sensitive aryl chlorides and amines that were previously unsuccessful substrates for Cu-catalyzed C–N coupling. A detailed structure–activity relationship study was used to uncover two key structural features that contribute to this efficacy. First, steric repulsion caused by a methyl substituent induces a conformational change that opens up additional space for ligand deprotonation and oxidative addition. Second, the trifluoromethyl groups create electrostatic interactions between the ligand and aryl chloride substrates that facilitate oxidative addition via through-space ligand–substrate interaction.
Asymmetric Total Syntheses of Hetidine-Type C20-Diterpenoid Alkaloids: Spirasines V and VI, Spiradine D, and the Proposed Structures of Spirafines II and III
F. Yao, Y. Wu, Y. Sheng, K. Yu, P. Rao, J. Xuan* & H. Ding*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c13564)

The authors describe a divergent strategy toward the asymmetric total syntheses of five hetidine-type C20-diterpenoid alkaloids: spirasines V and VI, spiradine D, and the proposed structures of spirafines II and III. Crucial transformations include an Enders asymmetric addition, an oxidative dearomatization induced Diels–Alder cycloaddition, and a MHAT-initiated transannular radical cyclization. The heterocyclic rings were assembled by an efficient reductive cyclization sequence at a late-stage. This approach has enabled the total syntheses of these natural products in 17–20 steps from commercially available starting materials with high enantio- and diastereocontrol.
Total Synthesis of Annotinolide B via Sequential Quinoline Dearomatization
B. Duvvuru & M. W. Smith*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c14142) 🔓

The authors report the first total synthesis of the complex cyclobutane-containing Lycopodium alkaloid annotinolide B. This approach leverages a sequential quinoline dearomatization strategy that enables the transformation of this readily accessible heteroaromatic precursor to a tricyclic N-acyl dihydropyridone intermediate. Extensive studies aimed at forging the signature cyclobutane revealed a β-silyl acrylate to be essential for the success of a key [2+2] photocycloaddition reaction. Further functional group transformations and a final one-pot methylation/lactonization sequence furnish annotinolide B in 20 steps.
Metal- and CO-Free Carbonylation of Alkyl Iodides
E. Le Saux,† M. Mathis,† G. Panizzolo & B. Morandi*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c13505)

The authors report a new method for the carbonylation of alkyl iodides under photochemical conditions. The process relies on a simple aryl formate reagent, synthesized in one step from readily available chemicals and capable of releasing CO along with a phenolate species in the presence of a mild base. The photoactivity of this phenolate is harnessed to activate alkyl iodides via single-electron transfer and generate alkyl radicals that add to CO and ultimately offer access to carboxylic acids and amides.

Contemporary Strategies in SmI2 Catalysis: A Reagent Reborn
J. I. Mansell, C. Romano & D. J. Procter*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Accepted (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202519678) 🔓
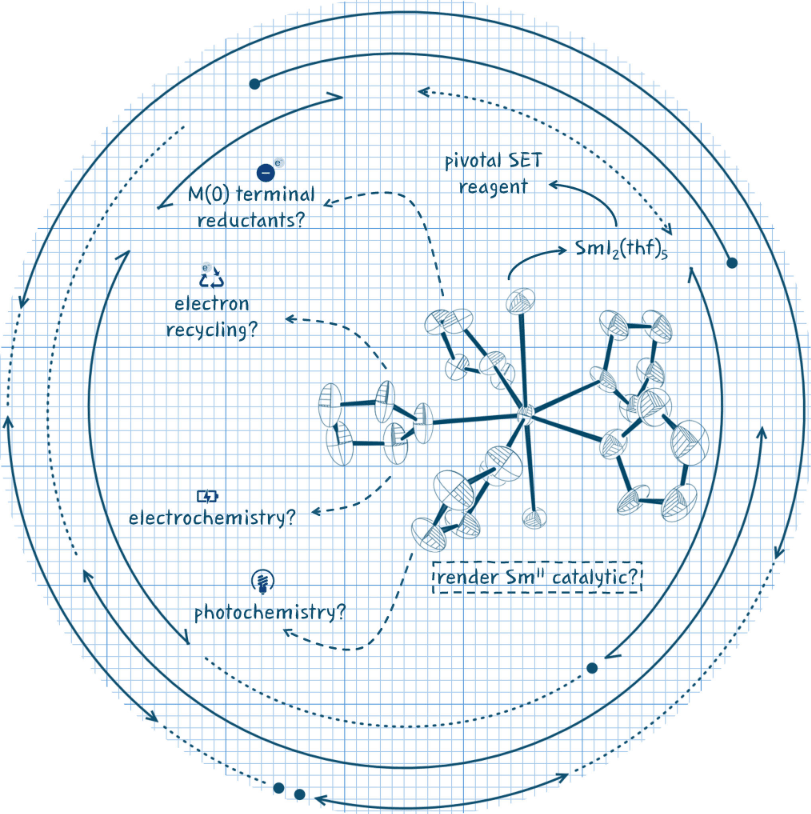
The rich chemistry of the single electron transfer reagent SmI2 has been widely exploited in synthesis. Recent years have seen significant progress in SmI2-catalysis, with provision of a suite of systems that may evolve to provide the efficiency, practicality, and generality needed for widespread adoption. This minireview provides a critical evaluation of strategies for SmII -catalysis and maps out a course that will complete the reinvention of SmI2 as a tool for sustainable catalysis.

Ambiphilic Cross-Coupling
B. Roh, B. A. Williams & J. Cornella*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-74b8f) 🔓
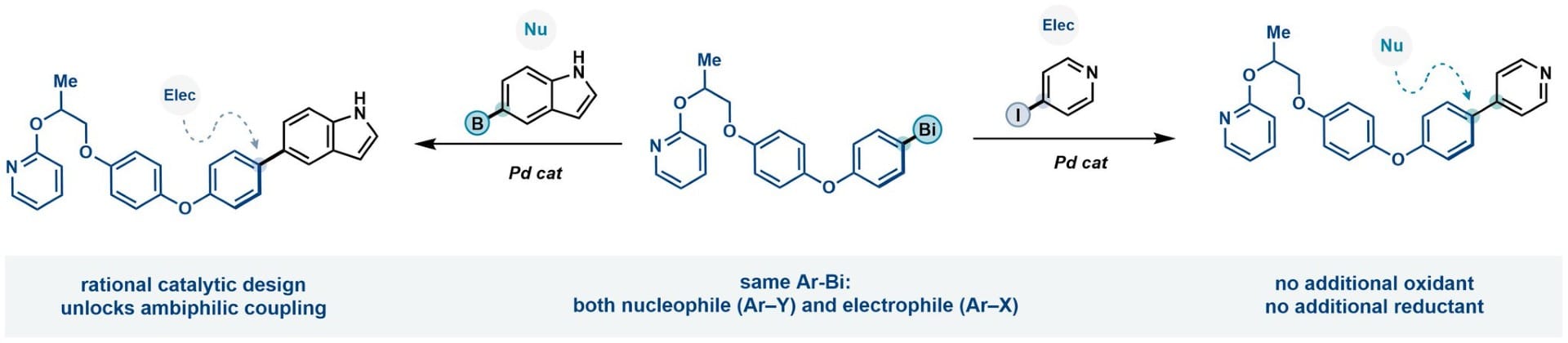
Cross-coupling reactions traditionally permit the formation of Ar‒Ar bonds between an aryl nucleophile and an aryl electrophile under transition metal catalysis. The high selectivity of the myriad of couplings known to date relies on a tailored combination of nucleophilic and electrophilic coupling partners. Here, the authors report ambiphilic aryl-bismuth reagents that can behave as either nucleophiles or electrophiles in transition metal–catalyzed cross-couplings, fundamentally breaking from this dichotomy in polarity. Their ambiphilic reactivity arises from their ability to engage in both oxidative addition and transmetalation processes with transition metal complexes, as demonstrated by stoichiometric and mechanistic studies.
Facile Trifluoromethylation of Arenes and Heterocycles via a Bench Stable Photocaged Trifluoromethylation Reagent
G. J. Rustin, V. Agarwal, P. I. Dalton, Z. Jiang, Z. Liu, I. G. Najor, B. Heydari, B. Heydari, N. J. Kuehl, V. Kumirov, M. T. Taylor* & Jeffrey L. Gustafson*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-ssqwg) 🔓
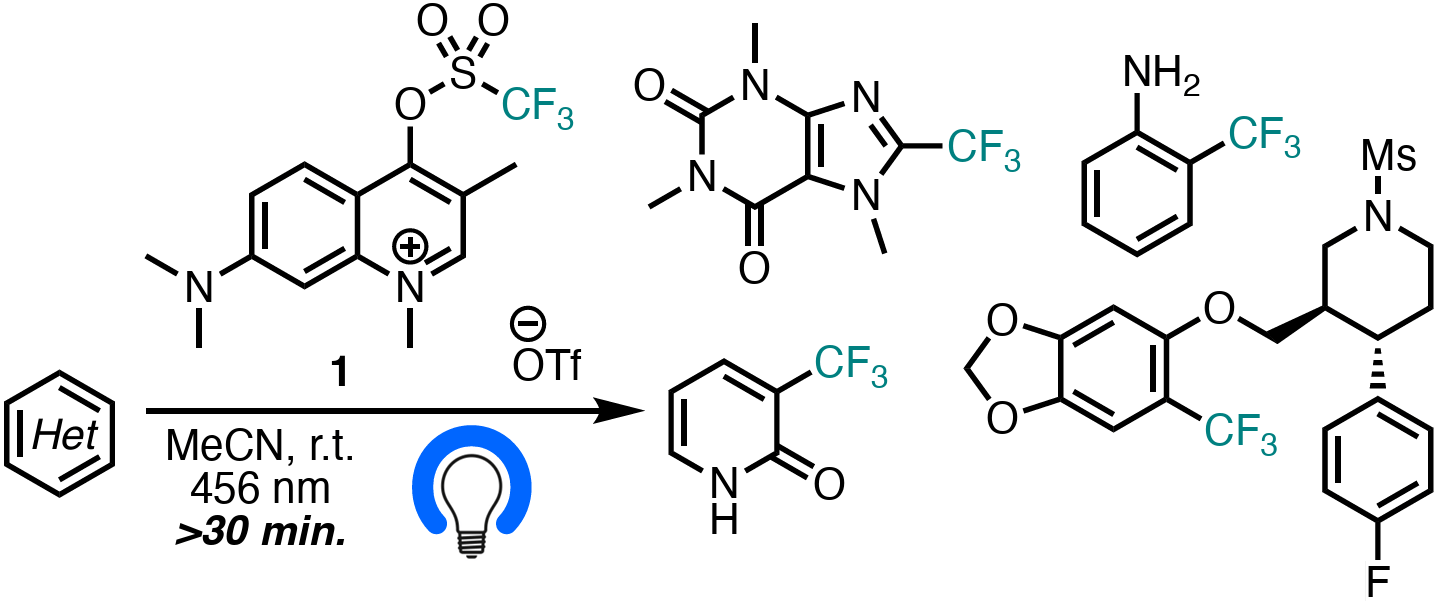
The authors report a simple radical aromatic trifluoromethylation process that utilizes a cationic, aromatic sulfonate ester as a trifluoromethyl radical photocage. This chemistry allows for the rapid and straightforward trifluoromethylation of diverse aromatics and heterocycles, including complex pharmaceuticals and natural products, with only substrate, photocage, solvent, and 456 nm light in minutes.
Ring-Opening Decarbonylative C(sp3 )–C(sp3 ) Cross-Electrophile Coupling of Cyclic Imides with Unactivated Alkyl Chlorides
N. J. Lentelink, P. M. F. Pânzar, N. A. V. Rowlinson & B. Morandi*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-3bcv2) 🔓

The authors report a nickel-mediated decarbonylative cross-electrophile coupling of N-Boc succinimides and glutarimides with unactivated alkyl chlorides. The transformation proceeds via selective endocyclic N–C(O) activation, which opens a new entry point into C(sp3 )–C(sp3 ) cross-electrophile coupling and, through incorporation of the ring-opened imide scaffold, establishes a highly modular platform to structurally diverse α- and β-substituted amides.

Scalable Transannular Bromocyclization Approach to Functionalized Bis-Heterobicyclo[3.n.1]anes
D. P. Wood,* N. Hernandez, J. A. Newman & R. E. Johnson*
Org. Lett. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c03802)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-76xt9) 🔓
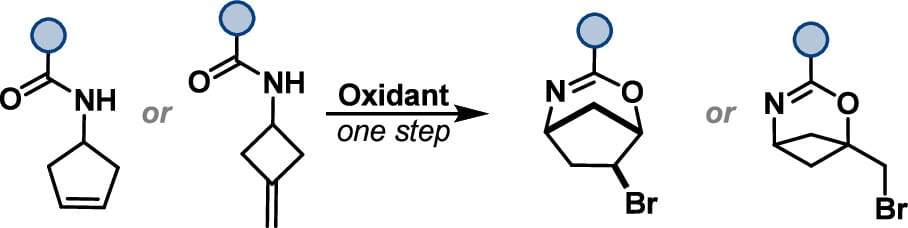
The authors report a scalable, transannular bromocyclization route to prepare functionalized 2-oxa-4-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-ene and 2-oxa-4-azabicyclo[3.1.1]hept-3-ene scaffolds from readily accessible alkene building blocks. This method demonstrates broad functional group compatibility and introduces a bromide handle for further diversification of the core.

We’ve been sending the newsletter out every Monday but is that the best day for you?
If your Mondays are usually busy and you’d prefer another day, let us know when works best. Equally, if Monday still works, drop a vote below! We can’t send the newsletter out individually but we can make sure that if most readers prefer another day, we can switch over.
Which day of the week would you prefer to receive the newsletter? |

Useful Knowledge & Creative Destruction
🏆️ Useful Knowledge & Creative Destruction. For most of human history, living standards barely changed. As Rutger Bregman notes in Utopia for Realists, if you were to drop an Italian peasant from 1300 into 1870s Tuscany, they would hardly notice a difference.
Historians estimate that the average annual income in Italy around the year 1300 was roughly $1,600. Some 600 years later—after Columbus, Galileo, Newton, the scientific revolution, the Reformation and the Enlightenment, the invention of gunpowder, printing, and the steam engine—it was… still $1,600. […] The past two centuries have seen explosive growth both in population and prosperity worldwide. Per capita income is now ten times what it was in 1850. The average Italian is 15 times as wealthy as in 1880.
In the span of two centuries, humanity escaped stagnation and entered an era of sustained economic growth. In 1820, 94% of the world’s population lived in extreme poverty. By 1981 that had fallen to 44%, and today it is under 10%. This year’s Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences honours those who explained why that happened: Joel Mokyr, Philippe Aghion, and Peter Howitt showed how innovation fuels sustained economic growth.
Mokyr identified that lasting progress depends on the accumulation of “useful knowledge”. Once people began to understand why inventions worked—not just that they worked—scientific insight and technological innovation could build upon each other in a self-sustaining cycle. Aghion and Howitt revealed that the economic mechanism known as creative destruction, where new technologies and firms continually replace old ones, drives productivity and growth. The Industrial Revolution made this clear: in the early 1800s, hundreds of thousands of British handloom weavers lost their livelihoods as power looms took over; yet the Revolution created far more industries and jobs overall. Progress is rarely painless in other words. However, it should be managed constructively so societies can protect workers using the right safety nets and retraining systems. Two centuries ago, science and innovation lifted humanity from centuries of stagnation. Progress doesn’t just destroy the old, it builds the foundation for what comes next.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply