- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Light, Catalyst, Reduction.
Light, Catalyst, Reduction.
💡 Why Cancer Might Protect the Brain from Alzheimer’s Disease

Monday 26th January – Sunday 1st February 2026 | Volume 3, Issue 4 |


Light-Driven Organocatalytic Birch Reduction for Late-Stage Drug Modification and sp3-Rich Spirocycle Synthesis
F. Schiel, L. di Martile, R. Coccia, A. Palone, M. Medrzycka, L. Kqiku, P. Neves, N. Matera, A. Misale* & P. Melchiorre*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c17373)

The authors report a practical organocatalytic system that enables Birch-type reductions of electron-rich benzenes (Ered = <−3.4 V vs. SCE) and heteroarenes under light irradiation and mild conditions using an indoline-2-thione anion catalyst. The protocol exhibits a broad substrate scope, including the late-stage functionalization of drug molecules bearing sensitive functional groups. Moreover, the synthetic utility of 1,4-dihydro products bearing an alcohol side chain was showcased through a two-step telescoped Birch reduction/spirocyclization sequence, granting streamlined access to sp3-rich spirocyclic scaffolds.

Engineered Aldehyde Dehydrogenases for Amide Bond Formation
L. Gao,† X. Qiu,† J. Yang,† K. Hu,† P. Li, W. Li, F. Gao, F. Gallou, F. Kleinbeck & X. Lei*
Science 2026 (DOI: 10.1126/science.adw3365)
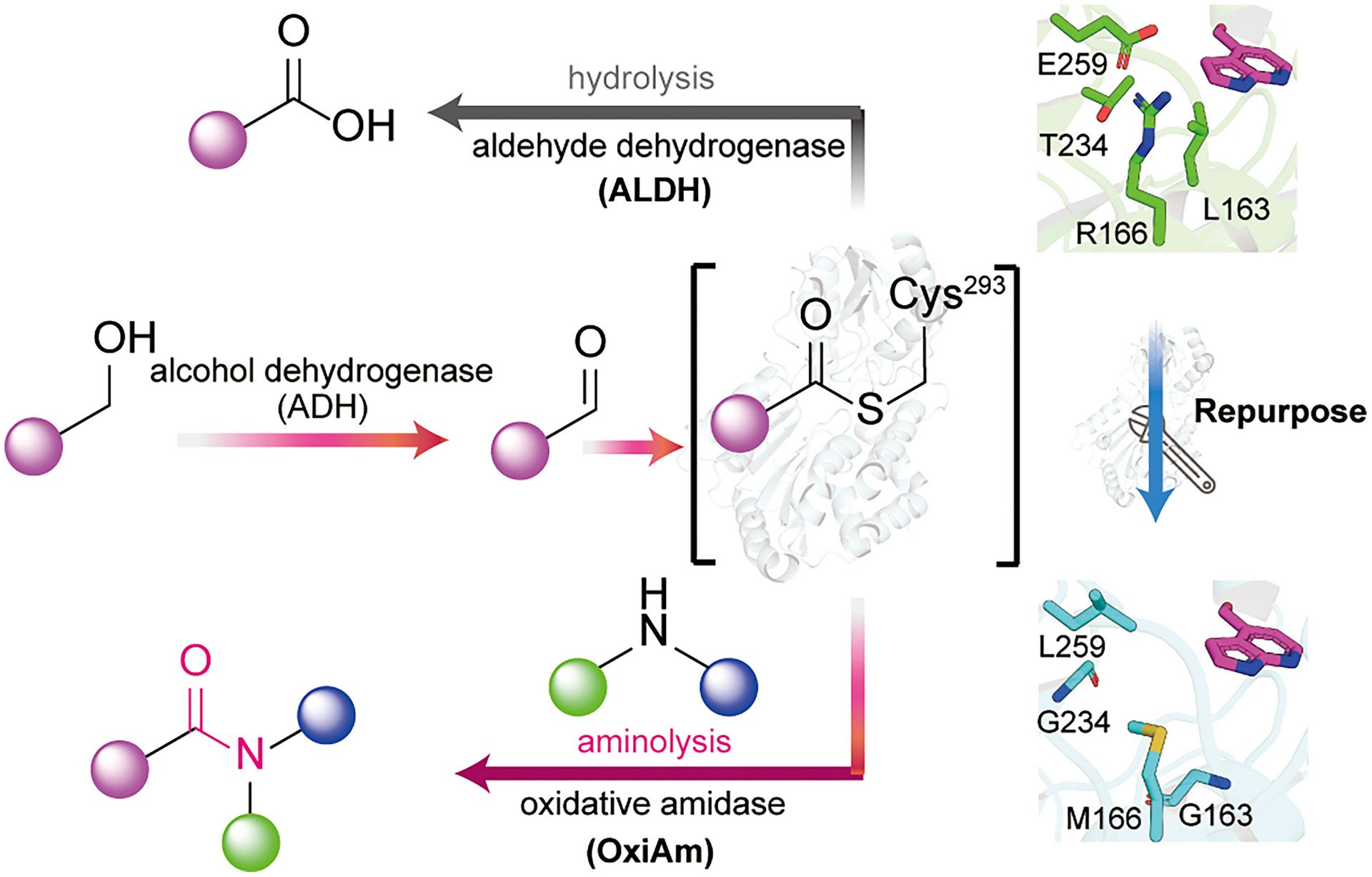
The authors repurpose aldehyde dehydrogenases into oxidative amidases by creating a more hydrophobic and spacious catalytic pocket for amines to capture the thioester intermediate. This biocatalyst efficiently facilitates the formation of amide bonds between diverse aldehydes and amines. A two-step enzymatic cascade to synthesize amides from broadly available aliphatic alcohols was also developed. This biocatalytic strategy enabled the redesign of synthetic routes for five drug molecules.

Photoinduced Benzene Ring Contraction of Arylhydrazines for the Synthesis of Fused Pyridines
K. Li, Y. Zeng, K.-H. Li, Y. Yang, J. Shen, H. Guo, Y. Tan, J.-J. Guo* & A. Hu*
Nat. Synth. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00976-4)
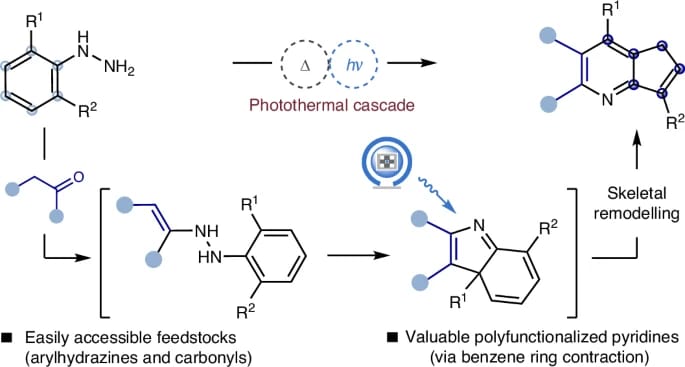
The authors present a photothermal cascade that unlocks the reactivity of the transiently generated light-absorbing intermediate formed during interrupted Fischer indolization. Complementary to arene ring expansion methodologies, this protocol offers a practical ring contraction approach for the modular synthesis of fused pyridines with good functional group tolerance and predictable regioselectivity.
Concerted 1,3-Migration Through Regiodivergent Consecutive 1,2-Rearrangements Using Palladium Catalysis
J. Gong, Q. Wang & J. Zhu*
Nat. Synth. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00979-1)

The authors report a concerted 1,3-migration strategy by integrating a palladium-catalysed semi-pinacol rearrangement with a 1,2-C/Pd(IV) dyotropic rearrangement. Two distinct 1,3-shift products can be selectively obtained by controlling the conformation of the Pd(II) intermediate, which can in turn be modulated by the metal’s supporting ligand. A key feature of this methodology is that the absolute configuration of the migrating group is retained, an outcome unachievable with existing strategies.

Divergent Photochemical Ring-Replacement of Isoxazoles
Y. Xu, L. Poletti, E. M. Arpa, B. Roure,* A. Ruffoni* & D. Leonori*
Nat. Commun. 2026, 16, 10234 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-026-68960-w) 🔓
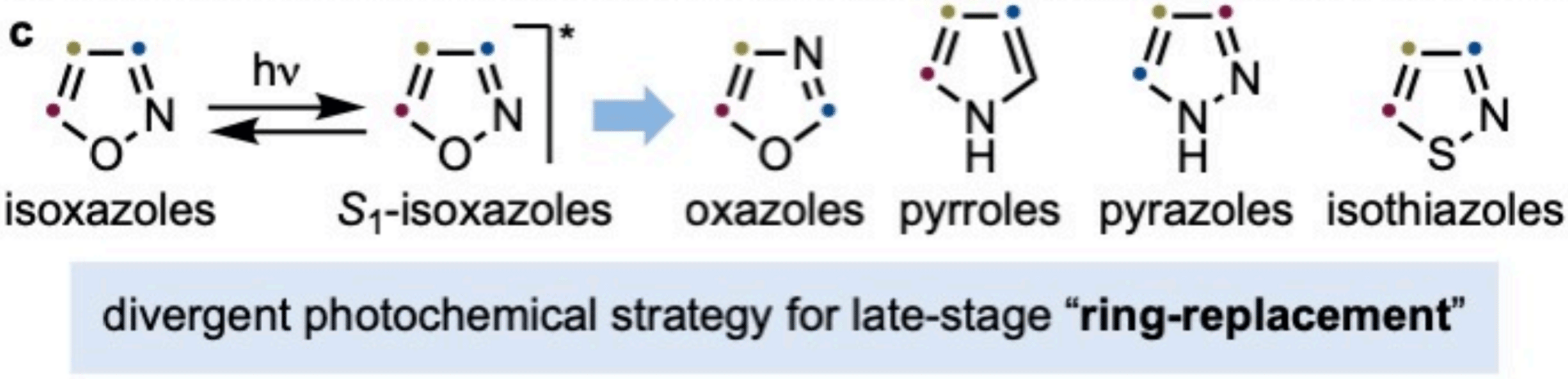
The authors report a photochemical platform for the selective conversion of isoxazoles into oxazoles, pyrazoles, pyrroles, and isothiazoles by exploiting excited-state reactivity. Starting from a successful isoxazole-to-oxazole transformation, position-sensitive reactivity was uncovered that prompted computational investigation. These insights guide a systematic reactivity survey and reveal a solvent-controlled deconstruction–reconstruction pathway via α-ketonitrile intermediates.
Evolution of Manganese Low-Energy Photoredox Catalysis from High-Energy Visible Light Photocatalysis
W. Yang,† Y. Song,† X. Yu,† M. Tian, Y. Lan,* Y.-N. Wang, X. Jiang, S. Liu, W. Zhang,* S.-J. Li* & L. Niu*
Nat. Commun. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-026-68837-y) 🔓

The authors enable manganese low-energy photoredox catalysis through the in situ assembly of simple Mn salts with inexpensive coordinating chemicals. The combination of Mn(acac)2, 2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-diamine, and TMSN3 forms a visible-light-absorbing system that, under blue-light irradiation, generates azido radicals to promote anti-Markovnikov hydroazidation of unactivated alkenes using H2O as the hydrogen source. Extending this strategy, Mn(acac)3 and TMSN3 in CH3CN/HFIP enable light absorption up to 850 nm, allowing selective aerobic hydroxyazidation of alkenes in a single step.

Development of Multiple Local Computational Models in Retrosynthetic Analysis: Total Synthesis of (−)-Deoxylimonin
L. M. Gharbaoui,† J. Eun,† Y. Zhao & T. R. Newhouse*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c21055)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-lj989) 🔓

This work describes the development of a de novo strategy to access the A,D-seco limonoids utilizing robust synthetic operations allowing for the synthesis of a characteristic member, deoxylimonin. The retrosynthetic strategy uses resilient chemistry for the assemblage of a key carbocyclic tricycle in only 8 synthetic maneuvers. This intermediate is then amalgamated through a modern variation on the classic combination of ring cleavage and formation using an oxa-Michael reaction as a key synthetic operation. Two discrete local computational models were developed and rapidly integrated into the design stages of retrosynthetic analysis.
Concise Synthesis of Deoxylimonin
J. Bao,† L. Yao,† H. Tian & J. Gui*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c21054)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-23nhc) 🔓

The authors present a concise synthesis of the flagship member of limonoids, deoxylimonin, by a bioinspired skeletal reorganization approach. Key features of this synthesis include a stereoconvergent radical polyene cyclization to assemble the 6/6/6 tricyclic system, an oxime-directed Baldwin–Sanford oxidation to hydroxylate the unactivated C7–H, a titanium-mediated intermolecular aldol reaction to introduce the 3-furanyl lactone moiety and two contiguous stereogenic centers, and a biomimetic transesterification/oxa-Michael addition cascade to install the tetrahydrofuran−δ-lactone-fused motif.
Engaging Unstabilized Alkyl Radicals with Pyridoxal Radical Biocatalysis: Enantiodivergent Synthesis of Aliphatic Non-Canonical Amino Acids
L. Cheng, J. Chen, Z. Bo, X. Zhang, P. Liu* & Y. Yang*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c16304)
Previously: BioRxiv (DOI: 10.64898/2026.01.21.700944) 🔓
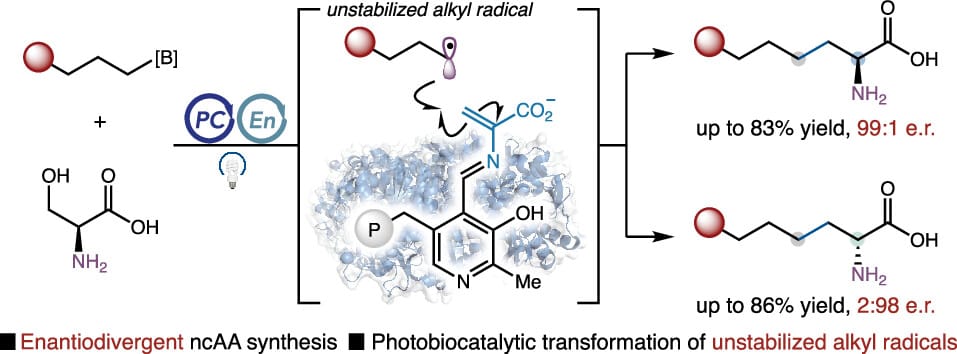
Through the repurposing and directed evolution of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent tryptophan synthases, an open-shell enzyme platform capable of intercepting transient alkyl radicals for the efficient and enantioselective synthesis of aliphatic noncanonical amino acids was developed. Engineering an orthogonal pair of radical PLP enzymes allowed unstabilized alkyl radicals, generated from diverse aliphatic organoboronates, to undergo dehydroxylative C(sp3)–C(sp3) coupling with a common ʟ-serine donor, affording either ʟ- or ᴅ-amino acids with excellent enantiopurity in an enzyme-controlled fashion.
Iridium-Catalyzed Borylation of Strong Alkyl C(sp3)–H Bonds of Sulfonamides Enabled by Triflyl Activation
S. Guria, A. Biswas, J. Das, X. Yan, S. Dey, J. Chaturvedi, G. Huang* & B. Chattopadhyay*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15739)

The authors report a strategy for sp3 C–H borylation of a wide range of acyclic and cyclic amines by incorporating trifluoromethanesulfonyl (triflyl) as an activating group and by employing a commercially available ligand under iridium catalysis. This method demonstrates highly selective borylation of primary C–H bonds at various positions (α-, β-, γ-, and δ-) with good to excellent isolated yield of the desired products.

Scalable Enantioselective Oxidation of Aliphatic N-heterocycles via Catalytic Hydride Abstraction
N. Le, J. Izquierdo-Ferrer,‡ F. Fan,‡ B. Górski, R. Smith, J. Masuda, J. Rein, N. G. Cowper, J. K. Widness, B. Cardinal-David, A. G. Doyle,* E. A. Voight* & S. Lin*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10001709/v1) 🔓

The authors report the enantioselective oxidation of N-protected cyclic amines to chiral lactams via asymmetric hydride abstraction by novel oxoammonium catalysts. This process employs a readily prepared amine catalyst precursor and is operationally simple, air-and water-tolerant, and highly selective across a broad substrate scope. This method streamlines the synthesis of key intermediates for bioactive molecules on preparative scale (up to 22 g lab scale and 10 kg plant scale) and provides rapid access to structural analogs of these medicinal agents.
👉️ For recent, related work by the same authors on “Desymmetrization of Meso-Pyrrolidines via Oxoammonium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydride Transfer” see here.
Enabling Access to sp3-Enriched Targeted Protein Degraders via Redox-Neutral Radical Cross-Coupling
P. Neigenfind, C. Gathmann, E. C. Cherney, C. G Parker & P. S. Baran*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10001725/v1) 🔓

This study presents a modular route to C3(sp3)–C(sp3)-linked glutarimides via a redox-neutral cross-coupling and palladium-catalyzed hydrogenation sequence. The two-step protocol is operationally simple, chemoselective, and tolerant of diverse functional groups. It delivers sp3-rich, three-dimensional scaffolds that access previously untapped chemical space. Preliminary studies of BRD4-targeting ligand-directed degraders derived from these scaffolds demonstrate Cereblon-dependent degradation of BRD4, highlighting their translational potential.
A General Photooxidation Platform for Alcohols via Transient Excited-State α-Keto Esters
R. L. Pilkington & A. Polyzos*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10001617/v1) 🔓

The authors report a general alcohol oxidation platform in which phenylglyoxalate α-keto esters act as visible-light-activated, traceless oxidation devices, converting primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones without external photocatalysts, metals, or stoichiometric oxidants. The protocol shows broad functional group tolerance and supports late-stage oxidation of complex scaffolds, including pharmacophores, carbohydrates, steroids and a peptide. Practicality is further demonstrated through in situ alcohol activation and efficient continuous-flow scale-up.

Quantitative Scale for the Nitronium Cation-Donating Ability of Electrophilic Nitrating Reagents
L. Yu, Y. Li* & X.-S. Xue*
J. Org. Chem. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.5c02563)
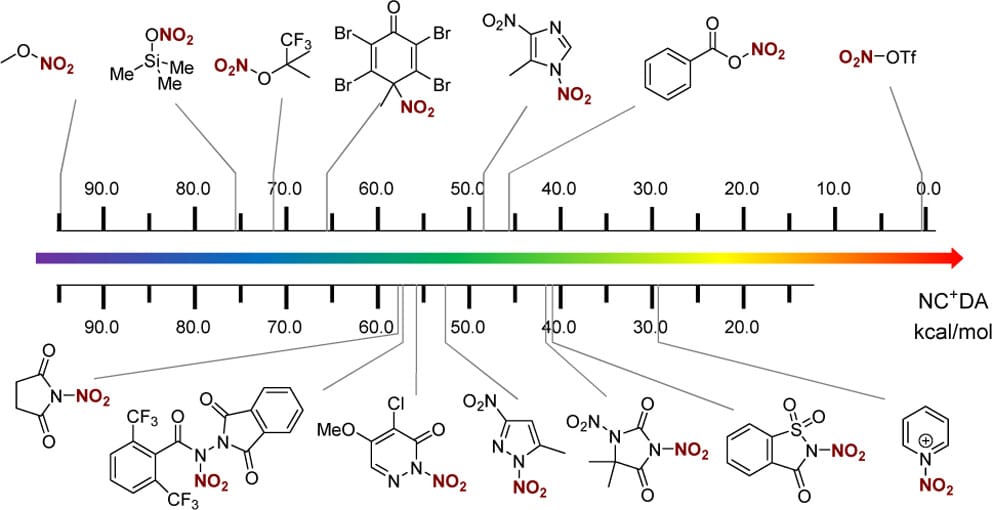
The authors present a comprehensive computational investigation of the nitronium cation donating ability (NC+DA) of more than 50 reagents, including alkyl nitrates, nitric anhydrides, N-nitropyridinium salts, N-nitropyrazoles, N-nitroamides, pyridazinone derivatives, and other heterocyclic systems. The results enable the establishment of a systematic NC+DA scale and reveal detailed structure–reactivity relationships influenced by electronic and steric factors. Guided by this scale, several potential N-nitroamide-type reagents with lower NC+DA values than existing nitroamides were designed.

A Protective Cancer Protein
🧠 A Protective Cancer Protein. For years, researchers have noticed an unusual trend: people with cancer appear to be less likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease. Large population studies support this observation—including a 2020 meta-analysis of more than 9.6 million individuals, which reported an 11% lower incidence of Alzheimer’s among people with a cancer diagnosis—but the biological basis has remained unclear.
Now, a study published in Cell offers a potential explanation. Working in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, Lu and colleagues show that cancer cells release a protein called cystatin C that can cross the blood–brain barrier and help to break down amyloid plaques, a defining feature of Alzheimer’s pathology. The researchers implanted lung, colon, or prostate tumours into mice genetically predisposed to Alzheimer’s disease. Strikingly, tumour-bearing mice developed far fewer amyloid plaques and performed better in memory tests than mice without cancer. Further experiments revealed that cystatin C binds to amyloid and activates TREM2, a receptor on immune cells in the brain, triggering clearance of the plaques.
The finding is notable because TREM2 has long been viewed as a promising but challenging target for Alzheimer’s disease with early clinical trials of molecules designed to activate TREM2 producing mixed results.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.
Reply