- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Insert. Delete. Synthesise.
Insert. Delete. Synthesise.
💡 The Year in Pharma: Science, Strategy, and a Shifting Global Landscape

Quick note: Next week’s issue (Monday 22nd December) will be our final edition of 2025 before the Christmas and New Year break. We’ll be back on Monday 12th January 2026, once journals have resumed publishing as usual, covering all new publications from 1st January onward.
Monday 8th December – Sunday 14th December 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 47 |


Unified Total Synthesis of C2-Symmetric Bis(cyclotryptamine) Alkaloids Utilizing a Single-Atom Insertion/Deletion Strategy
H. Yamagishi, D. W. Small & R. Sarpong*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15181) 🔓

The authors present a strategy for the synthesis of bis(cyclotryptamine) alkaloids inspired by methods for single-atom insertion/deletion. First, the synthesis of tetrahydropsychotriadine, an isomer of calycanthine, was pursued and achieved in 9 steps, which set the stage for the preparation of calycanthine, chimonanthine, and psychotriadine. These studies also provided the first access to a natural product bearing the pyrrolidinoquinoline scaffold, CPC-2, and a long-standing misassignment of the natural product dubbed isocalycanthine was resolved. En route to the synthesis of tetrahydropsychotriadine, a methodology for the construction of unprecedented diaryl-substituted cis- and trans-fused 5,5-bicycles using a photodecarbonylation was established.

Mechanochemical Synthesis of Organosodium Compounds Through Direct Sodiation of Organic Halides
K. Kondo,† M. Lowe,† N. Davison, P. G. Waddell, R. J. Armstrong,* E. Lu,* K. Kubota* & H. Ito*
Nat. Synth. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00949-7) 🔓

The authors report a mechanochemical protocol for the direct generation of organosodium compounds from cheap and shelf-stable sodium lumps and readily available organic halides under bulk, solvent-free conditions. These reactions generate an array of organosodium compounds in minutes, without special precautions against moisture or temperature control. These nucleophiles can be used directly for one-pot nucleophilic addition reactions with electrophiles and nickel-catalysed cross-coupling reactions. Furthermore, this mechanochemical approach enables the sodiation of inert C–F bonds in organic fluorides.

Total Synthesis of Aconicarmisulfonine A, a Sulfonated Diterpene Alkaloid
S. Ning & T. J. Maimone*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c17047) 🔓

Recently, Shi and Zhang isolated a new class of sulfonated diterpene alkaloids from the roots of Aconitum carmichaelii. These zwitterionic alkaloids possess several unprecedented new ring systems and displayed potent analgesic properties in preliminary pain model studies in mice. Here, the authors describe synthetic entry into this subclass of C20 diterpene alkaloids via a total synthesis of the most potent analgesic member, aconicarmisulfonine A, which features an unusual sulfonated bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane core.
Catalytic Enantioselective Cross-Nucleophile Coupling via Valence Tautomerism
Z. Zhang, A. Khosravi, J. A. Shah, K. P. Quirion, S. C. Yachuw, A. T. Poore, S. Tian,* P. Liu* & M.-Y. Ngai*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c16654)

The authors utilize one-electron valence tautomerism through a dual photoredox/nickel-catalyzed system to facilitate oxidant-free, enantioselective cross-nucleophile coupling (CNC). This method efficiently couples a diverse range of β-keto esters and amides with silyl enol ethers and allyl silanes, producing coupling products that feature a quaternary stereocenter with high stereocontrol.
Aryne Generation from Aryl Halides via Photothermal Red-Light Activation
C. Preston-Herrera, R. C. Devin, M. E. Matter & E. E. Stache*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c14686)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-4w6g6) 🔓

The authors report the generation of arynes from commercially available aryl or heteroaryl halides via photothermal conversion in air using red light. With photothermal conversion, a high-energy aryne intermediate is formed via inhomogeneous thermal gradients. Nitrogen nucleophiles then readily trap the aryne intermediate to forge C–N bonds. A wide range of readily available heteroaryl and aryl halides undergo amination in less than 20 min under red light irradiation of carbon black. Additionally, aryne trapping was demonstrated via a [4+2] cycloaddition, with a sulfur nucleophile, and a one-pot double amination with 1,2-dibromobenzene.
Boron-Enabled Stereoselective Synthesis of Polysubstituted Housanes
H. Fang, A. García-Camacho, H. S. Hwang, A. Sudsamart, C. G. Daniliuc, O. O. Grygorenko, I. Funes-Ardoiz* & J. J. Molloy*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c17624) 🔓

The authors report a boron-enabled strategy for the synthesis of polysubstituted housanes from nonsymmetrical dienes. A geminal diboron system ensures site-, regio-, and diastereoselectivity in an energy transfer-catalyzed [2+2] cycloaddition of nonsymmetrical dienes while also facilitating the mild generation of a cyclobutyl anion that triggers a stereospecific intramolecular annulation via conjugate addition, delivering complex housanes, with three defined exit vectors, in just two steps.
Electrochemical Dehydroxymethylative Functionalization of Unactivated Alcohols via Criegee–Kolbe Radical Relay
Y. Chen,† Y. Xu,† S. Zhang, X. Chen, F. Gan, X. Tan, K. Feng, X. Xiao, Z. Y. Cao,* M. Chen* & X. Kong*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c18031)

An electrochemical platform operating under mild, metal-free conditions leverages a hydrogen atom transfer (HAT)/O2–Criegee relay to convert various alcohols into one-carbon-shortened radicals, enabling dehydroxymethylative nitration, fluorosulfonylation, azidation, and phosphinoylation with broad functional-group tolerance and gram-scale practicality. Pairing the anodic radical generation with a cathodic Ni cycle further delivers C(sp2)–C(sp3) coupling, including the one-step methylation of aryl halides using ethanol as a feedstock methyl source.

Novel Sulfonium Reagents for the Modular Synthesis of Spiro[2.3]Hexanes and Heteroatom-Containing Analogues: Synthesis, Application, and Evaluation as Bioisosteres
P. Natho, A. Vicenti, F. Mastrolorito, F. De Franco, L. Walsh-Benn, M. Colella, E. Mesto, E. Schingaro, O. Nicolotti, A. Gioiello & R. Luisi*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202521633)

The authors report modular access to nine different spiro[2.3]hexane analogues, including underdeveloped 5-oxa-1-azaspiro[2.3]hexane and 1,5-diazaspiro[2.3]hexane motifs. This approach leverages novel cyclobutane-, oxetane-, and azetidine-substituted sulfonium salts, which can undergo Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky type reactions with alkenes, carbonyls and imines to provide access to the desired spiro[2.3]hexanes. The first comprehensive computational and predictive in silico evaluation of their bioisosteric potential is also reported, with validation provided by in vitro experiments.
Caylobolide B: Structure Revision, Total Synthesis, Biological Characterization, and Discovery of New Analogues
M. R. P. George,† L. A. Elsadek,† M. Deering, L. Costa de Almeida, J. L. Tyler, A. Noble, V. J. Paul, H. Luesch,* C. P. Butts* & V. K. Aggarwal*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202523117) 🔓

Marine polyhydroxylated macrolides’ drug discovery potential is limited by structural complexity and scarce material supply, hindering structure assignment, synthesis, and biological studies. Here, the authors present an integrated workflow that combines chemogenomic profiling, ultra-high-resolution NMR-guided structural revision and stereochemical assignment, and modular total synthesis to enable comprehensive interrogation of the caylobolide B family.
A para-Selective Kolbe–Schmitt Reaction
X. Liu, G. J. P. Perry* & D. Kong*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202522503) 🔓

Discovered over 150 years ago, the Kolbe–Schmitt carboxylation has established itself as one of the most well-known chemical reactions. However, the process often requires extreme pressures and high temperatures. Here, the authors present a unique para-selective Kolbe–Schmitt-type carboxylation that proceeds at relatively low temperatures and uses near equimolar quantities of a carboxylating agent.

C=C/N=O Metathesis Enables Oxidative Decarboxylation
B. B. Botlik, A. N. Vieira,‡ B. Mitschke,‡ F. Ruepp & B. Morandi*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-b0fgk) 🔓

The authors present an iron(II)-catalyzed C=C/N=O metathesis, and its application to the mild oxidative decarboxylation of carboxylic acids. The reaction proceeds under air in a one-pot fashion, utilizing readily available, inexpensive reagents, and features an earth-abundant, environmentally benign iron catalyst. The reaction exhibits broad functional group tolerance, is efficiently scalable, and its late-stage applicability was showcased through the streamlined oxidative decarboxylation of 12 drug molecules. Divergent and convergent reactivity was demonstrated relying on the complementary C=C/O=N metathesis counterpart providing access to imines instead of ketones, and the method was extended to the synthesis of esters from α-aryloxy and α-alkoxy carboxylic acids.
Visible-Light-Mediated Aryl Ketone Coupling with Vinyl Thianthrenium Salts Enables Formal Paternò-Büchi Reaction
S. A. Chamness, M. Liu,‡ J. B. Erdei,‡ T. M. A. Weise & C. S. Schindler*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-0kdn2) 🔓

The authors report a ketone–alkene coupling strategy that achieves formal Paternò-Büchi reactivity relying on the design principle of alkene radical anion formation from vinyl thianthrenium salts. Selective olefin reduction decouples reactivity from carbonyl redox properties, enabling the construction of 2-aryl, 2’-alkyl oxetanes that would otherwise be inaccessible by visible-light-mediated [2+2]-cycloadditions. Initial formation of β-hydroxy thianthrenium intermediates is followed by a subsequent cyclization to give 2,2’-disubstituted oxetanes under mild, visible light-enabled conditions.
👉️ For recent, complementary work on “A Unified Synthetic Approach to 2-Alkyl Azetidines, Oxetanes, Thietanes and Cyclobutanes from Unactivated Alkenes” by Silvi and co-workers, see: here.
Direct α-C–H Heteroarylation of Unprotected Primary Amines
G. D. Johnson, S. A. Corio, J. D. Grayson, J. D. Tibbetts, G. Ballantyne, Q. Cao, H. E. Askey, J. J. Bell-Tyrer, O. P. Datsenko, M. A. Graham, P. K. Mykhailiuk, J. S. Hirschi* & A. J. Cresswell*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-q5jr2) 🔓

The authors demonstrate that unprotected primary amines, when paired with SNAr-active azolyl chlorides, undergo selective α-C–H heteroarylation under dual photoredox–hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) catalysis. This protocol furnishes previously inaccessible N-unprotected α-azolyl amines, including sterically demanding α-tertiary motifs. Continuous-flow photochemistry further broadens the scope to highly SNAr-reactive azolyl chlorides by combining high photon flux with low-temperature operation to suppress rapid background N-arylation.
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of (E,E,Z)-Humulene Derived Natural Products
A. T. Saucedo, B. Valladares, D. A. Delgadillo, H. M. Nelson & A. R. H. Narayan*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-g158n) 🔓

The authors detail the first synthesis of (E,E,Z)-(10S)-hydroxyhumulene and elaborate this macrocycle through a chemoenzymatic route to (±)-deoxyeupenifeldin and neosetophomone B, and further accomplish the chemical synthesis of pughiinin A. The (E,E,Z)-(10S)-hydroxyhumulene was accessed via a selective oxidative double-bond isomerization from the (E,E,E)-humulene core. Additionally, when studying this macrocycle in subsequent hetero-Diels Alder (hDA) cycloadditions, it was observed that the (E,E,Z)-core imparted more biased diastereoselectivity when compared to previous studies of the corresponding (E,E,E)-core.
Triply Convergent Cross-Coupling of Aryl Halides, Aryl Boronic Acids, and Aryl Carbenes: Regulation of Transmetalation Timing by a Copper Co-Catalyst
Y. Ping, S. Li, Z. Deng, J. Zhou, P. Liu* & R. Y. Liu*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-wxsf2) 🔓
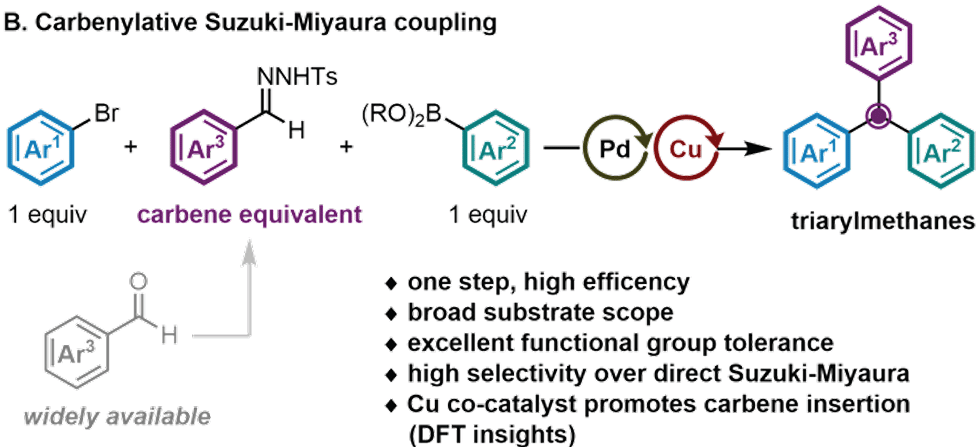
The authors report that a copper co-catalyst, combined with N-tosylhydrazones as general arylcarbene equivalents, allows a formal carbene insertion step to be embedded directly into the Suzuki–Miyaura manifold. This strategy enables the construction of two C–C bonds at a central methine and grants access to three-dimensional chemical space with broad substrate scope and excellent functional-group tolerance. The utility of this method is demonstrated through streamlined syntheses of pharmaceutically relevant scaffolds and analogues, alongside diverse post-derivatizations that highlight the versatility of this triply convergent platform.

The Year in Pharma
💊 The Year in Pharma. As 2025 draws to a close, C&EN’s Year in Pharma highlights a sector stirred by scientific momentum but shaken by geopolitical realignment. Cardiometabolism, oncology, and advanced modalities continued to dominate investment, while policy and regulatory shifts increasingly influenced how drugmakers operate.
Weight-loss therapeutics commanded attention with semaglutide and tirzepatide firmly established as blockbusters. Eli Lilly surpassed a $1 trillion market capitalisation and investors intensified their focus on next-generation cardiometabolic drugs. Oral GLP-1 programs multiplied, driving major partnerships and record financings, including Verdiva Bio’s $411 million Series A.
Oncology remained a cornerstone of biotech investment, with antibody–drug conjugates emerging as one of the year’s most sought-after modalities and driving the largest up-front licensing payments and venture rounds through the third quarter. Artificial intelligence continued to embed itself across the drug discovery pipeline, increasingly viewed as essential infrastructure rather than a standalone technology.
At the same time, US companies licensed 83 assets from Chinese developers in 2025, and Chinese programs now account for nearly one-third of global out-licensing value, underpinned by strong state support. Meanwhile, shifts in US policy added further complexity. Despite early expectations of deregulation, the Trump administration pushed aggressively on drug pricing and domestic manufacturing, prompting most large pharma companies to announce new US facilities to mitigate tariff risk. At the FDA, leadership turnover and workforce reductions strained regulatory capacity and added to industry uncertainty.
Following a period of financial strain across the global life sciences sector, the outlook for 2026 is cautiously optimistic, underpinned by advancing pipelines and signs of improving capital conditions.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply