- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Breaking the Rules
Breaking the Rules
💡 Happy Birthday Benzene

Monday 9th February – Sunday 15th February 2026 | Volume 3, Issue 6 |


Breaking the “Rule-of-Five” to Access Bridged Bicyclic Heteroaromatic Bioisosteres
Z.-X. Zhang, K. Shu, M. J. Tilby, M. J. P. Mandigma, Y. Guo, J. L. Tyler, A. Noble* & V. K. Aggarwal*
Nat. Synth. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-026-00990-0) 🔓

Bioisosteric replacement of (hetero)aromatic rings with bridged bicyclic hydrocarbons is an important strategy in drug discovery. Intramolecular [2+2] cycloadditions of unconjugated dienes provide access to such motifs but are governed by the “rule-of-five,” which dictates preferential formation of five-membered rings, limiting access to alternative ring sizes. Here, the authors introduce a visible-light-mediated intramolecular [2+2] cycloaddition of aza-1,6-dienes that enables selective formation of bridged over typically favoured fused bicycles to generate 6-azabicyclo[3.1.1]heptanes with substitution at every ring position. Exit vector analysis and comparison of the physicochemical and pharmacological properties of a 6-azabicyclo[3.1.1]heptane analogue of a piperazine-based drug demonstrate the scaffold’s potential in medicinal chemistry.

Transferable Enantioselectivity Models from Sparse Data
S. Gallarati,† E. M. Bucci,† A. G. Doyle* & M. S. Sigman*
Nature 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-026-10239-7)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-f5ddv-v2) 🔓

The authors report a descriptor generation strategy that accounts for changes in the enantiodetermining step as a function of catalyst and substrate identity, enabling the modeling of reactions across distinct ligand and substrate classes. To validate this approach, data were collected for enantioselective nickel-catalyzed C(sp3) couplings, and statistical models were trained using features derived from transition states and intermediates implicated in asymmetric induction. The resulting models enable optimization of underperforming examples within reported substrate scopes and generalize to previously unseen ligands and reaction partners.

Contra-Electronegativity Transmetallation Unlocks Alkene Carbomagnesiation to Access Quaternary Stereocentres
X. Ye,† B. Sun† & S.-L. Shi*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-026-02073-1)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-bz7dd) 🔓
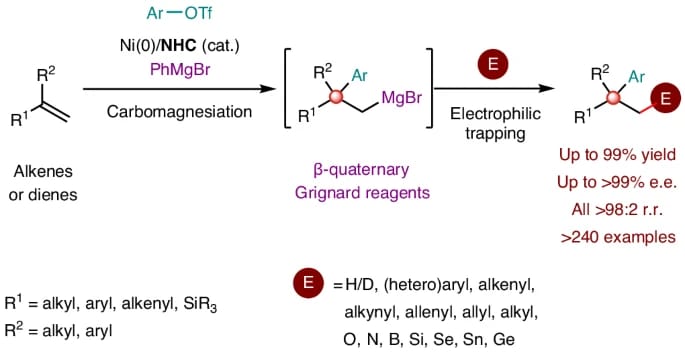
The authors report a nickel-catalysed carbomagnesiation strategy enabled by a rare contra-electronegativity transmetallation (Ni to Mg). This method provides efficient and modular access to β-quaternary Grignard reagents from 1,1-disubstituted alkenes and 1,3-dienes, using aryl triflates and PhMgBr as carbon and magnesium sources, respectively. The resulting organomagnesium intermediates participate in one-pot reactions with diverse electrophiles, affording stereochemically complex quaternary centres with high precision.
Asymmetric Synthesis of Enantioenriched Lactams from Cyclic Ketones via Beckmann Rearrangement
S. Zhong,† L. Xu,† M. Guo, D. Xie, Y. Lan* & Y. Xia*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-026-02068-y)

The authors report a chiral phosphoric acid-catalysed synthesis of enantioenriched five- to seven-membered lactams. This method uses prochiral cyclic ketones and readily available O-(sulfonyl)hydroxylamine reagents, proceeding via a Beckmann rearrangement with remarkable efficiency and stereocontrol, providing efficient access to chiral drug molecules.

Overriding Stereochemical Outcomes in Cyclase Phase Total Synthesis: Enantioselective Synthesis of Habiterpenol and Dasyscyphin A
L. Wu, L. H. Nguyen, L. Yan, H. Yin, N. Mizuno & A. W. Schuppe*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6c00141) 🔓

The authors report the enantioselective total syntheses of habiterpenol and dasyscyphin A. By exploiting a quaternary carbon stereocenter epimerization protocol, the intrinsic stereochemical bias of polyolefin cyclization reactions was overridden. Accordingly, the efficient and selective construction of the polycyclic scaffolds of both meroterpenoid natural products that bear an unconventional cis-hydrindane motif was achieved.
Total Synthesis of (±)-Dhilirolide U
H. R. Wilke, M. Fadel, K. J. Patej, J. P. Prohaska, J. Kastner, V. Avramenko, O. G. Gonzalez, R. Bal, M. C. Amberg, J. Ahmad, N. Nasiri, T. K. Jenny & E. M. Carreira*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c22734)
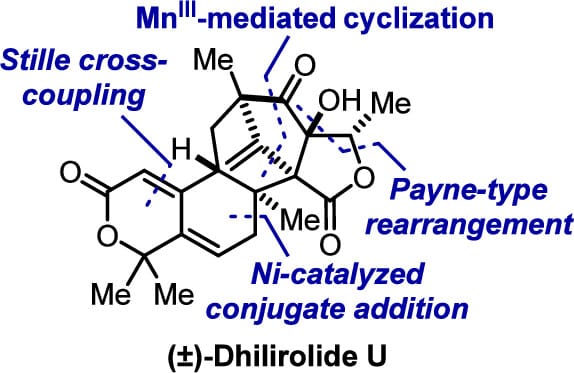
The authors report the first total synthesis of (±)-dhilirolide U, a highly oxidized meroterpenoid featuring a densely functionalized 6/6/6/5/5 pentacyclic skeleton. The synthesis is enabled by a MnIII-mediated cyclization sequence and a Payne-type rearrangement cascade that together construct a γ-lactone-fused bicyclo[3.2.1]octane. An intramolecular Ni-catalyzed conjugate addition installs the vicinal quaternary carbon centers, setting the stage for formation of the tetrahydroisochromenone subunit and completion of the synthesis.
The Catalytic Asymmetric Mukaiyama–Michael Reaction of Silyl Ketene Acetals with Cyclic Enones: Short Routes to Jasmonates
R. Xu, H. Zhou, H. Y. Bae, V. N. Wakchaure, L. Baldinelli, I. F. Leach, G. Bistoni, P. Kraft & B. List*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c20804) 🔓

A silylium imidodiphosphorimidate (IDPi) Lewis acid catalyst enables a broadly applicable organocatalytic asymmetric Mukaiyama–Michael addition of moderately electrophilic cycloenones with enol silanes, affording 1,4-adducts in up to 98% yield and >99:1 e.r. At 0.05 mol % catalyst loading, the reaction scales to 167 g of product with 96% catalyst recovery. The method accommodates a wide range of enones and silylated nucleophiles, allowing streamlined access to key jasmonates and related valuable targets.
Synthesis of Spiro Carbocycles via Methyl β-C(sp3)–H Functionalization of Cyclic Aliphatic Acids
T. Sheng,† Z. Zhao,† Y. Lu,† N. Chekshin & J.-Q. Yu*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6c01021)

The authors report a ligand-controlled β-C(sp3)–H methyl olefination and arylation that enables efficient syntheses of spirocyclic lactones, spiro-3,4-dihydrocoumarins, and spirocyclic ketones. Computational and deuterium incorporation studies suggest that MPAA (mono-N-protected amino acid) and MPAThio (mono-N-protected amino aryl thioether) ligands reverse the preference for methylene C–H activation observed with bidentate pyridone ligands by favoring the activation of primary C–H bonds. Furthermore, sequential functionalization of both methyl and methylene C–H bonds in cyclic acids was realized to significantly expand the structural diversity of carbocycles.
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Two Aromatized Halicyclamines
Z. D. Firestone, T. A. Grigolo, F. G. Pernichelle & J. M. Smith*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c22699)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-m9ksj) 🔓

The concise and divergent syntheses of the marine alkaloids (+)-tetradehydrohalicyclamine B and (−)-epi-tetradehydrohalicyclamine B are disclosed. Each synthesis requires ten steps and hinges on several key transformations including an enantioselective organocatalyzed Michael addition, a macrocyclic aza-Wittig ligation, and reagent-controlled stereodivergent lactam reductions to assemble their core molecular frameworks.

Nickel-Catalyzed Aryl Group Interconversion: A Non-Equilibrium Strategy for Aryl Nitrile Synthesis
H. Tanaka,† E. Moriya,† Y. Onozawa & J. Yamaguchi*
JACS Au 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.5c01654) 🔓

The authors describe a nickel-catalyzed aryl group interconversion between aromatic esters and 2-cyanopyridine. The process is driven by a decarbonylative ether formation step, which provides an irreversible pathway and establishes nonequilibrium conditions, eliminating the need for excess electrophiles. This method accommodates a wide range of aromatic esters and delivers pharmaceutically relevant nitriles with high efficiency.
Amine-to-Halogen Exchange Enables an Amine–Acid Etherification
A. McGrath,† S. K. Das,† E. Shim, A. Outlaw, S. Zhumagazy, H. R. Nodeh, J.-F. Brazeau, Z. Shi, J. D. Venable, C. Gelin, P. M. Zimmerman & T. Cernak*
JACS Au 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.5c01528) 🔓

The authors report an amine–acid etherification reaction that proceeds via a facile amine–halogen exchange and an ester-selective reduction. The method employs free aliphatic amines and carboxylic acids to form C(sp3)–O ether bonds directly. This method allows a diverse range of readily available alkyl amines and acids to be transformed into synthetically valuable alkyl ethers. The reaction is suitable for late-stage diversification and provides straightforward access to medicinally relevant α-deuterated ethers. Furthermore, the deamination strategy can be extended to other nucleophiles, enabling the synthesis of phenolic ethers and a range of halide products from amines.

Anomeric Amides: Valuable Reagents in Synthetic Organic Chemistry
A. Garg, J. Vigier, H. Lebel* & T. Besset*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2026, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202525799) 🔓

Enabling late-stage transformations and skeletal editing, anomeric amides have recently emerged as powerful synthetic tools. Due to their unique properties, these amides have been employed in reactions ranging from amination to halogenation. This minireview provides an overview of recent progress in using anomeric amides across a variety of synthetic transformations.

Decoding C–O vs. C–C Bond Selectivity in Nickel-Metallaphotoredox Carboxylic Acid Cross-Coupling
M. T. Findlay,† F. Lukas,† K. Yamazaki, G. Hopsort, B. Martin, S. Allmendinger, M. Furegati, P. Gabriel, E. H. Tiekink, T. A. Hamlin* & T. Noël*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10002040/v1) 🔓

Understanding how catalytic systems dictate product selectivity is crucial for advancing sustainable cross-coupling chemistry. While nickel–photoredox dual catalysis has unlocked C–C and C–O bond formation from carboxylic acids and aryl halides, the mechanistic origins of this divergence have remained elusive. Here, the authors combine systematic experimentation with DFT calculations and electrochemical analysis to uncover the key parameters that govern whether C–C or C–O bonds are formed. Halide identity of the aryl electrophile was shown to exert a decisive influence: iodides strongly favor esterification via a low-barrier reductive elimination pathway, bromides promote decarboxylative C–C coupling, and chlorides, with prohibitively high C–O barriers, yield exclusively C–C products.
Development of a Practical Copper-Catalyzed C–N Cross-Coupling for Heteroaryl Chlorides and Base Sensitive Substrates
A. McGrath* & D. Lehnherr*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.15000029/v1) 🔓

The authors report a new ligand for Cu-catalyzed C–N cross-coupling of (hetero)aryl chlorides with a broad range of nitrogen nucleophiles, including primary, secondary and α-branched amines, amides, hydrazines, ammonia surrogates, NH-heterocycles, and base-sensitive substrates such as aminomethyl-functionalized azoles. Both aryl and heteroaryl halides, including pyridyl and pyrimidyl chlorides, serve as competent coupling partners. Key reactivity trends of azole methanamines, as a function of azole identity and isomer, were elucidated through a direct comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous C–N cross-coupling conditions using 42 nucleophiles in parallel library synthesis.
α-Fluoroamines: Myth or Reality?
V. Levterov, O. Shablykin, O. Stashkevych, V. Kokhalskyi, V. Konashuk, I. Sadkova, O. Shevchuk, P. Borysko & P. K. Mykhailiuk*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10002101/v1) 🔓

Since 1985, scientists have been chasing aliphatic α-fluoroamines. Yet, these structures are unstable due to rapid dehydrofluorination. Here, the authors have shown that minimal structural modification—incorporation of a CH2-group—into the elusive α-fluoropiperidine provides a stable α-fluoroamine. This previously nonexistent chemical compound class has been comprehensively studied, characterized, and used in a medicinal chemistry project.

Room-Temperature Decarboxylative Amination of Electron-Deficient (Hetero)Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
R. Basnet, K. Golian, J. Sampson & J. M. Hoover*
Org. Lett. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c05346)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-0jbfd) 🔓
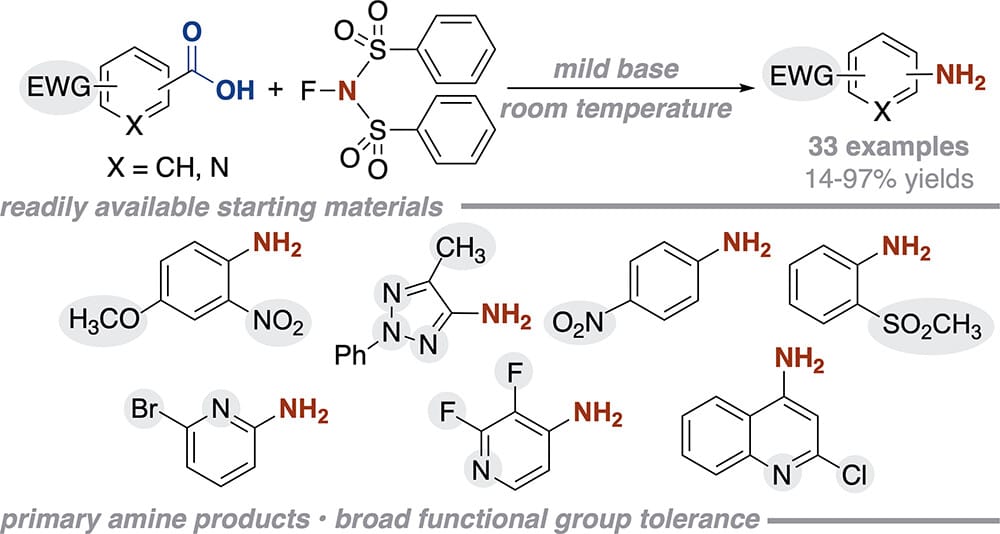
The authors report a room-temperature decarboxylative amination to generate a wide array of primary (hetero)aromatic amines mediated by N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide (NFSI). The broad functional group tolerance of this reaction enables efficient amination of biologically relevant small molecules. Mechanistic studies suggest that NFSI provides access to an activated sulfonimide intermediate, a functional equivalent to acyl azide intermediates, while avoiding the hazards associated with organoazides.

Benzene at 200
🎂 Benzene at 200. In 1825, Michael Faraday first isolated benzene from the fractional distillation of illuminating gas produced from whale and fish oil—making chemical history in an era when distillation alone could secure your place in the annals of chemistry (and, thankfully, without resorting to the distillation methods of Hennig Brand). The unusually pure hydrocarbon obtained, initially named bi-carburet of hydrogen, was meticulously characterised, promptly published, and largely forgotten. Faraday did not know that this simple by-product would become one of chemistry’s most consequential molecules. Now, on its 200th birthday, C&EN has published a fascinating feature tracing the history of the infamous aromatic.
☕️ Ditching Decaf. A large study published in JAMA has found that caffeinated coffee and tea intake is associated with lower dementia risk. Researchers analysed data from over 130,000 participants, tracking outcomes for up to 43 years, during which 11,033 dementia cases were documented. Participants were divided into four groups based on intake; those in the highest consumption group (top 25%) had an 18% lower dementia risk than those in the lowest group (bottom 25%). Moderate intake, around 2–3 cups of coffee daily, showed the strongest association. Notably, decaffeinated coffee showed no significant association, implicating caffeine rather than other coffee constituents.
💻️ WRN Breakthrough. Be sure to catch the German Chemical Society’s next Medicinal Chemistry webinar on Thursday 26th February, featuring Dr. Momar Toure of MOMA Therapeutics discussing the “Discovery of MOMA-341, a chemically distinct, potent and selective covalent inhibitor of Werner Syndrome Helicase (WRN) in clinical development”.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply