- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- Amines → Alkyls in 10 Minutes
Amines → Alkyls in 10 Minutes
💡 Uncovering a Missing Element in Alzheimer's Disease

Monday 4th August – Sunday 10th August 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 31 |


Deaminative Giese-type Reaction
P. Ma, Z. Cui & H. Lu*
Nat. Chem. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01888-8)

The authors present an approach to integrate nitrogen-atom deletion into the aza-Michael reaction, thereby redirecting the classical pathway from C(sp3 )–N bond formation to C(sp3 )–C(sp3 ) bond construction. Leveraging commercially available O-diphenylphosphinylhydroxylamine as an efficient nitrogen-deletion reagent, this method enables a wide variety of primary aliphatic amines to serve as alkyl sources in couplings with structurally diverse electron-deficient olefins. This Giese-type reaction proceeds under mild conditions, achieves completion within 10 min and exhibits broad functional-group compatibility.

Diastereodivergent Synthesis of Multi-Substituted Cycloalkanes
Z. Li,† D. Liu,† G.-W. Gao, P.-W. Chen, Y. Li, X. Zeng, Z. Li, X. Lu* & Y. Fu*
Nat. Chem. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01885-x)

The authors report a cobalt-catalysed process for the diastereodivergent synthesis of multi-substituted cycloalkanes. By strategically manipulating ligands, the diastereodivergent hydroalkylation of methylenecyclohexanes has been achieved. The process is capable of synthesizing all isomers of disubstituted cyclohexanes and piperidines, as well as multi-substituted cyclohexanes.

Organocatalytic meta-C–H Hydroxylation of Azaarene N-Oxides
Z.-C. Li, D. Tian, Z.-Q. Wang, P. Yuan & H. Wu*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c07423)
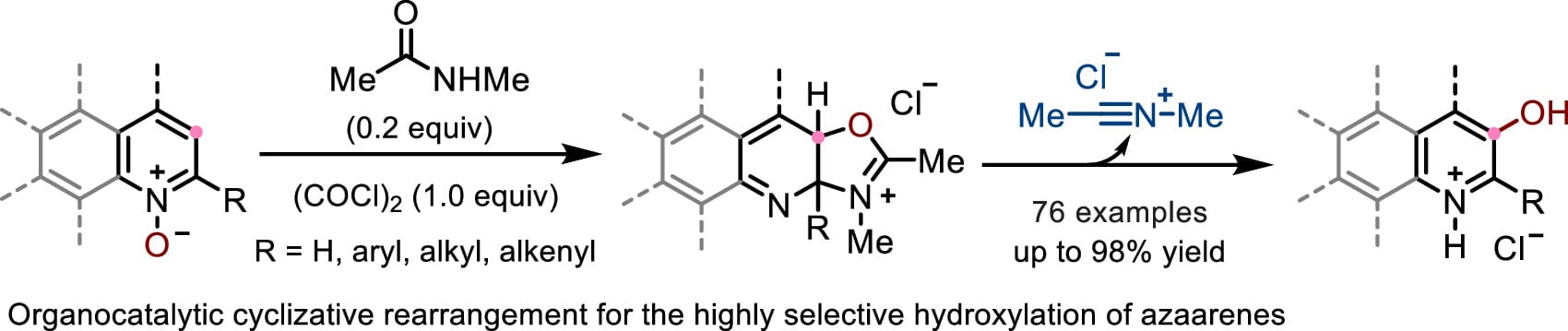
The authors report an organocatalytic thermodynamically driven cyclizative rearrangement that enables highly site-specific meta-hydroxylation of azaarenes with excellent chemoselectivities. Specifically, a nitrilium ion—formed in situ from the reaction of N-methylacetamide with oxalyl chloride—serves as a highly efficient catalyst, enabling a range of azaarene 1-oxides to undergo a stepwise 1,3-oxygen transfer, leading to the formation of the corresponding 3-hydroxylated derivatives. The transformation features column-free operation, a broad scope, and applications to the late-stage meta-hydroxylation of pharmaceutically relevant compounds was also demonstrated.
Total Synthesis of (−)-Neocucurbol C Enabled by Pattern Recognition and MHAT Cyclization
L.-P. Zhong, C. Gudeman, J. Zhen, O. A. Wanasinghe, J. Hellmig, M. J. E. Collins, J. Bacsa, A. Adibekian* & M. Dai*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08224) 🔓

The authors report an asymmetric total synthesis of (−)-neocucurbol C, a diterpene natural product possessing a unique 6/6/5/5/6 polycyclic skeleton and nine stereocenters. Pattern-recognition analysis led to the chiral pool molecule (+)-nootkatone as the starting material with the extra isopropenyl group removed by Kwon’s hydrodealkenylative bond fragmentation. Other key steps include: (i) a Suzuki–Miyaura cross coupling to introduce the E ring precursor, (ii) an oxidative dearomatization cyclization to form the oxa-bridge, and (iii) a metal-catalyzed hydrogen atom transfer (MHAT)-initiated reductive radical cyclization to complete the framework. In addition, cytotoxicity evaluation of (−)-neocucurbol C and its synthetic intermediates against multiple cancer cell lines identified new lead compounds with promising anticancer activity.
Concise Syntheses of Harziane Diterpenoids by Merging Local Desymmetrization and Radical Retrosynthesis
J. Wu,† J. Bao,† J. Deng,† H. Tian & J. Gui*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09579)
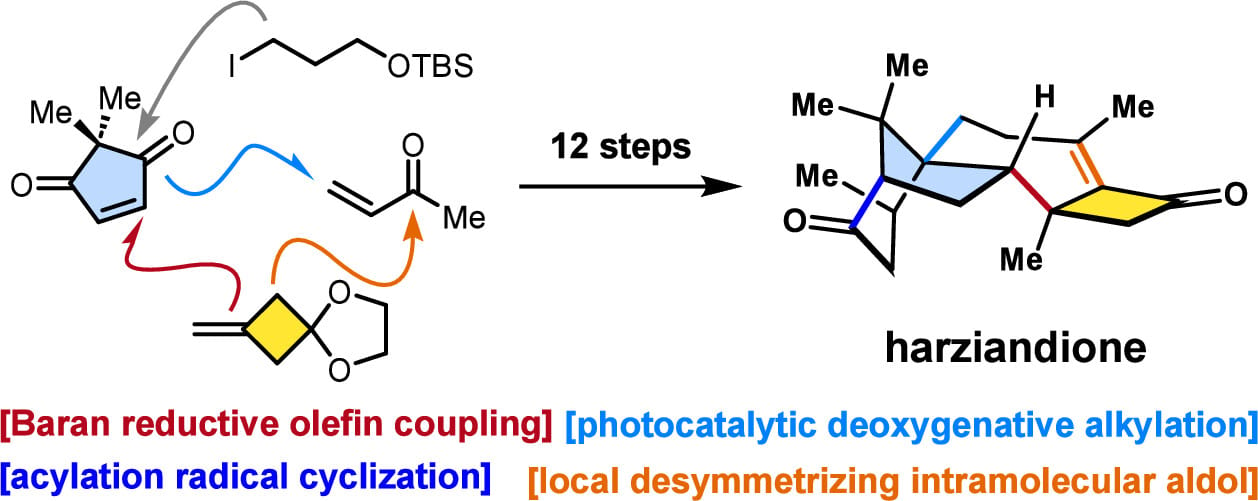
Harziane diterpenoids possess a highly caged 6/5/7/4 core framework and four contiguous stereocenters, including two quaternary ones. Here, the authors report an efficient strategy to rapidly access harziane diterpenoids by merging local desymmetrization and radical retrosynthesis. The strained bicyclo[5.2.0]nonene motif was installed using a local desymmetrizing intramolecular aldol reaction with high diastereotopic group selectivity, while the bridged [3.2.1] ring system and three contiguous stereocenters were rapidly forged by means of three strategic radical fragment couplings.
Total Synthesis of (+)-Pierisketone B
Q. Gu, G. D. Walby, M. D. Wood & S. F. Martin*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c08617)

The authors report the first total synthesis of (+)-pierisketone B, a bioactive diterpene that possesses a unique tetracyclic 7/5/6/5 carbocyclic framework and five contiguous stereocenters, two of which are quaternary. The synthesis features a Pauson Khand cyclization to generate the bridged tricyclic core, a hydroxyl directed hydrogenation of an allylic alcohol to create the cis-fused hydrindanone, and a Mukaiyama aldol followed by a cyclization involving addition of a vinyl anion to a proximal ketone group to produce the A ring.
Tech-Enhanced Synthesis: Exploring the Synergy between Organic Chemistry and Technology
S. Bonciolini,† A. Pulcinella† & T. Noël*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c10303) 🔓

This perspective showcases how modern tools, ranging from continuous-flow reactors and electrochemical cells to photochemical technologies, biocatalysis, mechanochemistry, and self-driving laboratories, are reshaping the way chemists design, perform, and optimize reactions. Through selected case studies, the authors highlight how these technologies not only solve specific reactivity and process issues but also open new avenues for reactivity discovery and chemical innovation.

Skeletal Remodeling of Pyridines Through Nitrogen Atom Transposition
C. Jing,† H.-M. Jiang,† Q. Yan, F. Huang, J. Sun, L.-P. Xu* & H. Wei*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202512288)

The authors present a skeletal remodeling strategy that enables the transformation of pyridines into corresponding anilines via Lewis acid-catalyzed nitrogen atom transposition. The methodology was demonstrated across a range of complex pyridine derivatives and several commercially available drugs.
Radical Borylation of Alkyl Bromides by Photoinduced Halogen-Atom Transfer
C. R. Schull,† M. J. McGill,† Á. Renteria-Gómez, P. Mukherjee, S. B. Tyndall, A. H. Shoemaker, M. R. Wasielewski, O. Gutierrez* & K. A. Scheidt*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202510162) 🔓

The authors report a metal-free radical borylation strategy of various alkyl bromides utilizing a photoinduced silyl radical to mediate a halogen-atom transfer process. This method demonstrates broad utility and functional group tolerance among various primary, secondary, and tertiary unactivated alkyl bromides and can facilitate the functionalization of pharmaceutically relevant motifs.
Catalytic 1,2-Migratory Insertion in a Bismuth Redox Platform: Reductive Arylation of Aldehydes
X. Liu, H. W. Moon, D. Spinnato, M. Leutzsch & J. Cornella*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202510360) 🔓

The authors report a catalytic defluorinative arylation of aldehydes with (per)fluoroarenes facilitated by a pincer-based PheBox-Bi(I) under mild conditions. The protocol features various novel aspects in bismuth redox catalysis; namely, (i) a catalytic 1,2-aryl migratory insertion to forge a C–C bond, (ii) an unprecedented example of multicomponent reaction through four elementary organometallic steps at a Bi center, and (iii) an unusual strategy for Bi(I) compounds regeneration via O–Si reductive elimination.

Direct Access to Acylboranes via Formal Condensation of Carboxylic Acids with Ligated Boranes
C.-Y. Cai, C. Hu, R. R. Merchant & T. Qin*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-jv72f) 🔓

The authors report a radical-based C(acyl)–B cross-coupling strategy that enables a “formal condensation” between carboxylic acids and easily accessible ligated boranes. The success of this transformation relies on the use of a phosphonite ligand, which achieves an optimal balance between the stability and reactivity of the borane moiety. This method demonstrates a broad substrate scope with high practical utility, and its strategic value has been highlighted through diverse downstream derivatizations of the resulting acylborane compounds.
Pd-Catalyzed Azidation of Aryl (Pseudo)Halides
S. Li, P. Onnuch & R. Y. Liu*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-fvbnw) 🔓

The authors report an effective Pd-catalyzed method for the synthesis of aryl azides from aryl bromides and aryl triflates using sodium azide. A variety of heterocycles, along with a numerous aryl electrophiles incompatible with existing approaches, undergo efficient azidation.
Photocatalyzed Hydrogen Atom Transfer Enables Multicomponent Olefin Oxo-Amidomethylation Under Aerobic Conditions
M. Lepori, D. I. Ioannou, J. P. Barham* & T. Noël*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-whxc3) 🔓

The authors report a novel photocatalyzed three-component oxo-amidomethylation of aromatic olefins under aerobic conditions, enabling the synthesis of N-(γ-oxopropyl)amides via simultaneous incorporation of two orthogonal functional groups across the alkene C=C bond in a single step. This cascade protocol demonstrates compatibility with a broad range of aryl olefins and amides, as well as efficient scalability.
Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (–)-Verrucarol
M. H. Powers,† J. F. McCleerey Jr.,† J. W. Bacon, J. McNeely & J. A. Porco Jr.*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-fmd1f) 🔓
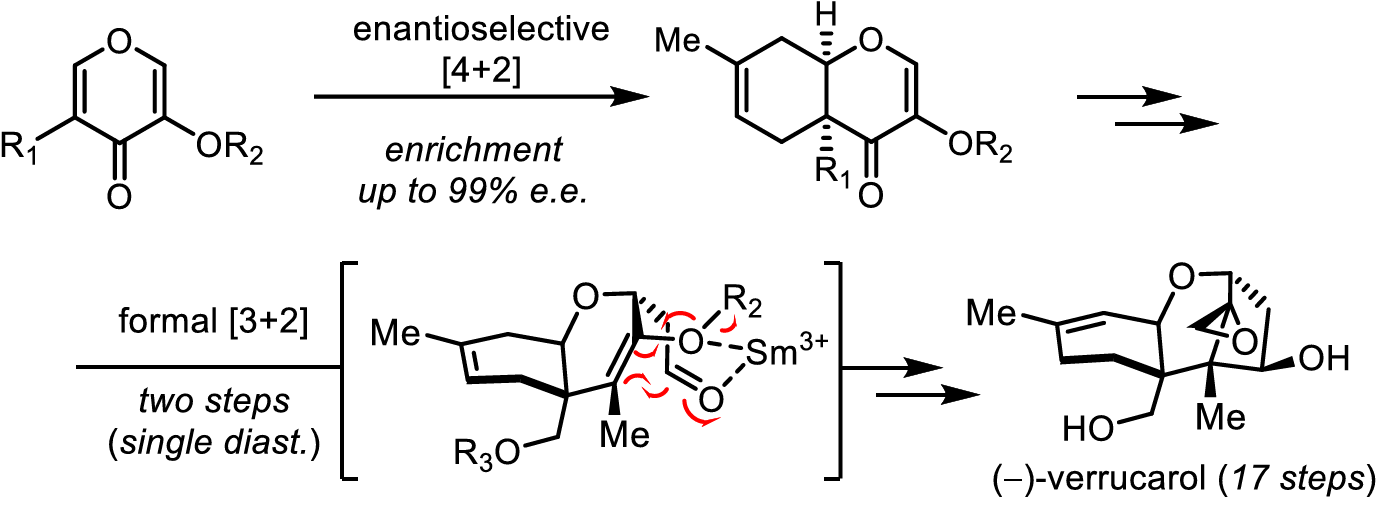
The authors disclose a concise, asymmetric synthesis of (–)-verrucarol, the natural product precursor of bioactive trichothecene macrocycles including verrucarins A and J. Historically, enantioselective construction of the 6/6/5 (A/B/C) ring system of the 12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-ene (EPT) core has represented a significant challenge. This architecture was constructed beginning with a chiral Lewis acid-catalyzed, enantioselective [4+2] cycloaddition to afford a cis-fused A/B ring fragment. Final C-ring closure was achieved by a diastereoselective 5-endo-trig cyclization, thereby completing a formal [3+2] annulation over two steps. Alkene transposition and hydroxyl-directed epoxidation completed the shortest asymmetric synthesis of (–)-verrucarol to date.

Recent Advances in Nonprecious Metal Catalysis
D. C. Cabanero, A. M. D. Reyes, X. Ju, X. Ma, J. L. Payne* & S. Radomkit*
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.5c00191)

This Perspective is part of a continuing review series that is published within the alliance among AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. The purpose of this article is to highlight the myriad of applications for nonprecious metal catalysts, specifically highlighting copper, cobalt, iron, and nickel. The utility of these metals, alongside their low cost and sustainable feedstocks, makes them ideal reagents. To underscore the advantages of nonprecious metal catalysis, the authors have highlighted transformations that are of interest to synthetic chemists.

Nitrilation of Carboxylic Acids by PIII /PV -Catalysis
S. Z. Ali, N. A. Manno, J. Shen, A. Schenker, J. M. Lipshultz, N. A. White* & A. Radosevich*
Chem. Sci. 2025, Accepted (DOI: 10.1039/D5SC05216E) 🔓

A mild and catalytic method for the direct conversion of carboxylic acids into their corresponding nitriles is reported. In contrast to common nitrile preparations that rely on hazardous cyanide and cyanogen precursors, the protocol employs a PIII /PV -catalyzed “oxidation-reduction condensation” approach to effect iterative amidation/retro-Ritter reaction of carboxylic acids with 1-phenethylamine. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and aromatic carboxylic acids all undergo nitrilation, including several pharmaceuticals and natural products.

Deaminative Cyanation of Anilines by Oxylanion Radical Transfer
D. Behera,† T. Schulte,† A. Altun, M. Leutzsch, F. Neese & T. Ritter*
Org. Lett. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c02410) 🔓

The authors report a straightforward methodology for direct deaminative cyanation of anilines via aryl diazonium salts as fleeting intermediates. The approach leverages the kinetic stability of nitrate and copper cyanide, iron’s ability to facilitate nitrate reduction, and appropriate relative rates to ensure the product-forming kinetic reaction pathway despite several thermodynamically favored, undesired reactions. Insight into the previously unappreciated nitrate reduction mechanism by simple sulfur-based reductants, such as SO2, is presented.

News you’ll want to read.
If you enjoy reading these short highlights on synthetic organic chemistry but are looking for a more general newsletter that provides quick, insightful updates about global and business news, I’d recommend checking out Morning Brew ☕️
Their newsletter is partly what inspired me to start this one and I’ve been reading it almost daily for a really good overview of what’s happening in the world 👇️
Business as usual? No thanks.
The problem with most business news? It’s too long, too boring, and way too complicated.
Morning Brew fixes all three. In five minutes or less, you’ll catch up on the business, finance, and tech stories that actually matter—written with clarity and just enough humor to keep things interesting.
It’s quick. It’s free. And it’s how over 4 million professionals start their day. Signing up takes less than 15 seconds—and if you’d rather stick with dense, jargon-packed business news, you can always unsubscribe.

Old Element, New Trick
🧠 Old Element, New Trick. A groundbreaking publication in Nature has found that restoring natural lithium levels in the brain may protect against—and even reverse—Alzheimer’s disease. The study, led by Bruce Yankner and colleagues at Harvard Medical School, offers new hope for the more than 55 million people living with dementia worldwide, the majority of whom have Alzheimer’s.
The team discovered that lithium levels were significantly depleted in regions of the brain affected by Alzheimer’s and perhaps more strikingly, the metal was found to be trapped within amyloid plaques (one of the disease’s characteristic hallmarks) leaving less available for essential brain functions. In mouse models, lithium deficiency led to more amyloid build-up, greater accumulation of tau tangles, and accelerated cognitive decline, mirroring patterns seen in humans.
The researchers also identified a concerning feedback loop: less lithium → more amyloid → even less lithium. However, they found a way to disrupt this vicious cycle with simple lithium orotate, a lesser-known form of lithium. Unlike lithium carbonate (commonly used to treat bipolar disorder), lithium orotate is less likely to be sequestered by amyloid plaques. In mice, low-dose lithium orotate reversed brain damage and restored memory. Even healthy control mice exhibited improved memory after treatment.
Lithium orotate, a simple and inexpensive compound, would be a massive shift from current anti-amyloid antibody therapies used to slow cognitive decline. Clinical trials will be essential to confirm these findings in humans; however, as lithium is an element and cannot be patented, major pharmaceutical investment is unlikely. Public or academic funding will be crucial to moving this line of research forward.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.


Reply