- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- [4+2–1]
[4+2–1]
💡 Science vs. Sceptics: Who’s Steering U.S. Vaccine Policy in 2026?

Welcome to the first edition of Synthesis Spotlight for 2026!
To begin the year, this issue looks back to Thursday 1st January and highlights key papers published over the past two weeks.
Thank you for reading, let’s get into it 👇️
Thursday 1st January – Sunday 11th January 2026 | Volume 3, Issue 1 |


Leveraging Triatropic Rearrangements for Stereoselective Skeletal Reshuffling
Y. Niu,† Y. Chen,† M. Zhou, H. Zeng, K. Wang, P. Yu* & Z. Dong*
Science 2026, 391, 171–178 (DOI: 10.1126/science.adw3340)

The authors report a class of pericyclic reactions, called triatropic rearrangements, wherein three σ-bonds are broken concomitantly with the formation of two σ-bonds and one π-bond, all in a single transition state. Within this mechanistic manifold, carbon-oxygen bonds in epoxides are stereoselectively converted into carbon-carbon bonds in a process mediated by organoboron reagents. Epoxycycloalkanes undergo highly chemo-, regio-, and stereoselective carbon migration to furnish ring-contracted products with broad generality. This strategy also enables enantioselective 1,2-hydride migrations for linear epoxide substrates. The combination of this ring contraction protocol with [4+2] cycloadditions provides a distinct “[4+2–1]” strategy for the stereoselective construction of complex cyclopentanes in a modular fashion.

Ferrioxalate Photocatalysis: A Multitasking Platform for Reductive Iron Catalysis
C. Bernabeu,† S. Adalid,† S. Colombo, N. Cironis, P. P. Sen, K. Okuno & F. Juliá*
Science 2026, 391, 84–89 (DOI: 10.1126/science.aeb1702)
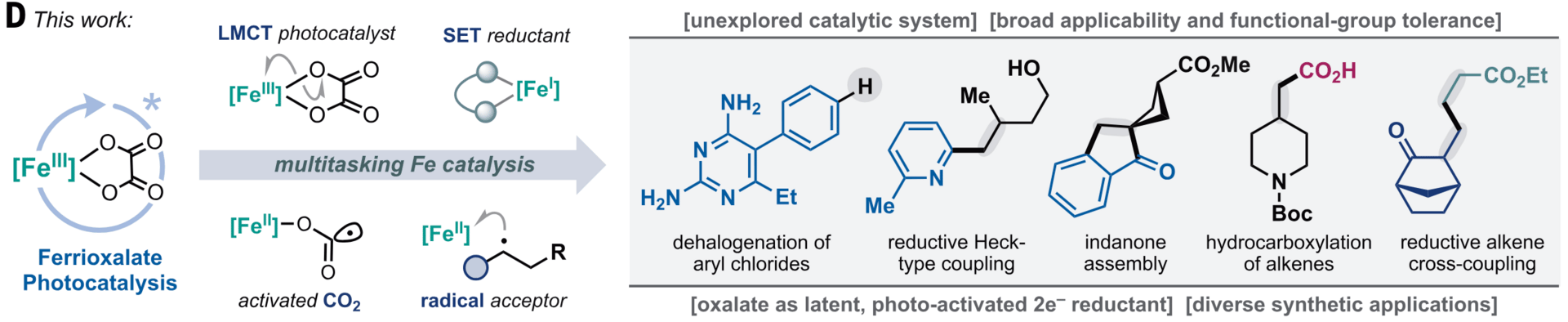
Iron’s abundance motivates its use in sustainable catalyst systems that offer complementary reactivity compared to precious metals. However, the challenging reduction of benchmark iron salts to active species hinders their application in reductive transformations. Here, the authors report a photochemical strategy that exploits ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) excited states of iron oxalate complexes to harness oxalate salts as latent terminal two-electron reductants in iron catalysis. This activation mode enables transformations previously inaccessible to iron catalyst systems and demonstrates synthetic utility across diverse reductive transformations using readily available building blocks with high chemoselectivity.
Access to Four-Membered Cyclic Sulfinamides by Energy Transfer Catalysis
D. Zhai, B. A. Williams, L. R. E. Pantaine, Y. Chen & M. C. Willis*
Science 2026, 391, 202–207 (DOI: 10.1126/science.aec3158)

Synthetic transformations that advance through excited states proceed by unconventional mechanistic pathways and deliver products not accessible using ground-state chemistry. The breadth of these transformations is constrained by the range of molecules—and particularly the functional groups—that can deliver productive excited states, with most methods using functional groups that were defined over 100 years ago. In this work, the authors show that N-silyl sulfinylamines can undergo synthetically useful excited-state reactivity accessed using energy transfer catalysts and visible light. These intermediates were exploited in reactions with alkenes to form four-membered cyclic sulfinamide products. The reactions are efficient and broad in scope, and the products are advanced to sulfonamides as well as four-membered cyclic sulfonimidamides.

Electrochemical Defluorinative Matteson-type Homologation
T. L. Cheung,† Y. Li,† P. Zhang, Z. Yang, Y. Quan* & H. Lyu*
Nature 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-10002-4)

The Matteson homologation, developed in 1980, elongates carbon chains by insertion into a C–B bond and typically involves three steps: carbanion formation, nucleophilic addition to an organoboron species, and boronate rearrangement, often requiring cryogenic temperatures and air- and moisture-sensitive reagents. Here, the authors present a one-pot electrochemical Matteson-type homologation that combines these steps through electroreductive defluorination and boronate rearrangement, eliminating the need for organolithium reagents or cryogenic conditions. Trifluoromethylarenes are employed as carbenoid precursors for the first time, broadening the scope of the Matteson reaction.

Homologative Alkene Difunctionalization
M. Kim,† S. Y. Ahn,† S. Kim,† J. Won, D. Kim & S. Y. Hong*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02037-x)

The authors report a strategy that integrates single-carbon insertion into established alkene functionalization methods, redirecting vicinal difunctionalization toward direct access to 1,3-difunctionalized products. The transformation is enabled by a methylene dication equivalent, iodomethylthianthrenium salt, which under photocatalytic conditions converts alkenes into linchpin 1,3-dielectrophilic intermediates. These intermediates allow efficient incorporation of nucleophiles at distal positions. The method exhibits broad functional-group tolerance and is well suited to pharmaceutical and late-stage applications, providing access to a diverse range of 1,3-difunctionalized products, including azetidines, 1,3-diazides, and 1,3-dihalides.
Direct Enantioselective C(sp3 )–H Coupling of N-Alkyl Anilines via Metallaphotoredox Catalysis
W. Zu, X. Wan, H. Wu, J. Huo, C. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Huang, Z. Xu, Y. Xu, T. Li, J. Cheng, J.-L. Ye, C. Wang & H. Huo*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02018-0)

The authors report a metallaphotoredox-catalysed radical approach for the α-C(sp3 )–H arylation of N-alkyl anilines, introducing a simple, sterically hindered aryl ketone photocatalyst. This key innovation slows undesired back-electron transfer, enabling efficient α-anilinoalkyl radical generation. Using a chiral nickel catalyst, site-selective, enantioselective arylation of diverse N-alkyl anilines with (hetero)aryl halides was achieved with exceptional functional group tolerance, enabling modular functionalization of complex molecular structures.

Direct Oxygen-to-Sulfur Single-Atom Substitution of Oxazoles and Isoxazoles
C. Yun,† X. Chen,† H. Song, H.-M. Jiang, Z. Xia, L.-P. Xu* & H. Wei*
Nat. Synth. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00967-5)

The authors present a skeletal editing strategy that enables the direct conversion of oxazoles and isoxazoles into thiazoles and isothiazoles, respectively, using different catalytic approaches. For isoxazoles, an iron-catalysed single-atom substitution with Lawesson’s reagent is used, enabling a straightforward oxygen-to-sulfur transformation. In contrast, oxazoles use a Lewis acid, La(OTf)3, for the same substitution, highlighting distinct reaction mechanisms. Both strategies allow for the rapid diversification of bioactive compounds, generating complex thio-analogues with broad functional group compatibility.
Catalytic Asymmetric Activation of Bicyclobutanes
F. Shi, N. Frank, M. Leutzsch, C. Zhu, N. Tsuji & B. List*
Nat. Synth. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00951-z) 🔓
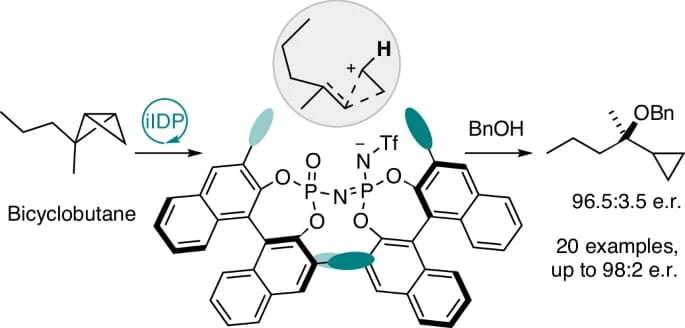
The authors disclose an organocatalytic asymmetric hydroalkoxylation of bicyclobutanes with alcohols to efficiently access tertiary cyclopropylcarbinyl ethers with high enantioselectivity (up to 98:2 e.r.). Enantiocontrol is accomplished through chiral recognition between the confined iminoimidodiphosphoric acid catalyst and the substrate, mediated by non-covalent interactions between a Lewis basic binding site of the confined anion and the polarized C–H bond of the cyclopropylcarbinyl ion intermediate.
👉️ For recent related work by List and co-workers on “Asymmetric Carbonium Ion Catalysis: The Intramolecular Hydroalkoxylation of Cyclopropanes”, see here.

Mapping the Undirected Borylation of C(sp3 )–H Bonds in Strained Rings
C. La, S. V. Ryabukhin, D. M. Volochnyuk & J. F. Hartwig*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c18839)

The authors report the borylation of alkyl C–H bonds in fused, spirocyclic, and polysubstituted cyclopropanes, cyclobutanes, azetidines, and β-lactams using the most recent generation of alkyl C–H borylation catalysts, achieving high diastereoselectivity. Importantly, reactions occur despite steric hindrance on adjacent carbon atoms, enabling the formation of more complex structures. The stoichiometry of the diboron reagent, the s-character of the C–H bond, and the arrangement of substituents influence reactivity and product distribution.
Cross-Electrophile Coupling of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Esters with Aryl Bromides Using an Inner-Sphere Homogeneous Reductant
K. Ganguli, A. R. Cruz, J. B. Diccianni, P. García-Reynaga* & D. J. Weix*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c18451) 🔓

Cross-electrophile coupling of aryl bromides and iodides with N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHP) esters is a valuable method for forming C(sp2 )–C(sp3 ) bonds. However, developing a broadly applicable approach remains challenging, particularly for electron-rich aryl bromides, which often require electrochemical tools or electron-rich NHP derivatives. Here, the authors report new conditions that overcome these challenges without specialized hardware through the use of a new class of homogeneous reductants: 1,4-bis(trialkylsilyl)dihydropiperazines (Si-DHP). These reductants rapidly reduce nickel(II) to nickel(0) and can be tuned to optimize performance. The method exhibits broad reactivity and is compatible with multiple solvents, addressing long-standing challenges for both small- and large-scale applications.
Nickel-Catalyzed Aryl Borylations: Opportunities and Challenges for Innovation
J. B. McManus,* G. P. Ahlqvist, C. R. Davis, L. de Lescure, V. N. Nair, A. R. Rötheli, B. J. Burke & J. S. Tedrow
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c16385)

The utility of aryl boronic acids and esters has led to various methods for their synthesis, from metal/halogen exchange to Pd-catalyzed Miyaura borylations and more recently, Ir-catalyzed C–H activations. Ni catalysis offers a more economical alternative, but also enables access to mechanistic pathways and substrates inaccessible with Pd catalysis. Despite successful demonstrations of Ni-catalyzed aryl borylations, the lack of general conditions and Ni-specific reaction design studies limits broader application. This Perspective discusses the current literature on Ni-catalyzed aryl borylation and suggests areas for further study. Advances in mechanistic insight, ligand design, high-throughput platforms, and machine-learning models will help establish reliable starting conditions, reducing the need for substrate-specific optimization and enabling the development of a well-understood suite of general reaction conditions that will make this mode of reactivity a competitive borylative strategy.
👉️ For a recent application by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Princeton University on the “Telescoped Nickel-Catalyzed Borylation-(Phenoxyimine)Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp2 )–C(sp3 ) Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling for Afimetoran Core Synthesis”, see here.
Divergent Total Synthesis of the Harziane Diterpenoids
P. M. Gemmel,† S. Kim,† Z. Zhou, J. R. Bossenbroek, N. Cercizi & S. A. Snyder*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c14490)

The harziane family of diterpenoid natural products possesses a unique 6/5/7/4 tetracyclic structure with up to six contiguous stereocenters, three all-carbon quaternary centers, and an array of oxidation patterns across the nearly 50 members that have been isolated since the first was reported in 1992. Here, the authors present a concise synthetic strategy using quaternary center analysis and common intermediate logic, achieving the synthesis of three family members as well as the proposed structure of a fourth, all in just 1–3 steps from a common intermediate. Three of these structures have been prepared for the first time and four other natural products were obtained formally from that same material.
Total Synthesis of (+)-Melicolone K Enabled by a Late-Stage Programmed C–H Functionalization
Z. Jia, P. Sun, T. Wang, Y. Sheng, C. Zhu, J. Xuan* & H. Ding*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c20001)

The authors report the first asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-melicolone K, featuring a late-stage programmed C–H functionalization, which comprises a Rh(II)-catalyzed γ-C(sp3 )–H amination and a cyclic sulfamate ester-directed γ-C(sp3 )–H prenylation. By incorporation of a Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation, a Wolff ring contraction, and a Ti(III)-mediated radical cyclization, the approach rendered concise and efficient access to this flagship prenylated natural product with good enantio- and diastereocontrol.

An “Inside-Out” Strategy Enables a 14-Step Total Synthesis of Hispidospermidin
C. Amber, T. Nakamura, M. Amoako, N. S. Settineri & R. Sarpong*
JACS Au 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.5c01567) 🔓

The authors report a 14-step protective group-free total synthesis of the polycyclic sesquiterpenoid alkaloid hispidospermidin, which exploits an early-stage complexity-generating bicycle formation to forge the carbon skeleton, followed by subsequent peripheral functionalizations. Uniquely, this strategy generates the primary complexity element, the bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane core, in the first step of the synthesis, whereas the three previous syntheses feature mid- to late-stage bicycle construction (total of 23–31 steps).

A Photochemical Strategy for Pyrazole to Imidazole Conversion
Y. Wei,† K. Kasama,† A. Igartua, D. B. Yildiz, A. Ceuninck, T. dos Santos, C. Büttner, D. Thevenet, M. Bossart, V. Derdau, M. Méndez, P. Jubault, T. Poisson,* B. Roure* & D. Leonori*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2026-68vcj) 🔓

The authors report a photochemical strategy that converts pyrazoles into imidazoles in a single step with broad functional-group tolerance and full retention of peripheral substitution. The reaction is effective across densely substituted and annulated systems and extends to pyrazolo[1,5-a]azines, a class of high-value heteroaromatics that have never previously been reconfigured. This photochemical strategy is readily translated to continuous flow, confirming its potential for scalable applications.
Development of a Tunable Photoreactor for High-Throughput Experimentation
R. Nsouli, H. N. Tran,‡ R. S. Sidhu,‡ H. Kaur, G. Galiyan & L. K. G. Ackerman-Biegasiewicz*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2026-kghtx) 🔓

The authors disclose the development of a tunable 24-well photoreactor that enables independent control of wavelength, light intensity, and irradiation time per well to efficiently screen light-driven reactions. In benchmarking studies of Fe visible light-induced homolysis (VLIH) chemistry, the platform demonstrated excellent reproducibility across wells, providing reliable comparison of parallel reaction outcomes. Moreover, the yield obtained in each well was comparable to the commercially available single-wavelength platforms. The plate successfully maintained room temperature even after a day of continuous irradiation and no significant light penetration was observed between wells. Additionally, the versatility of the photoreactor was demonstrated by screening a range of VLIH-mediated transformations, employing Fe, Ce, and Cu salts, each requiring distinct irradiation wavelength and time within the same plate.

Ligand Design Enables Cu-Catalyzed Etherification of Aryl Bromides Using Mild Bases
M. J. Strauss,† M. E. Greaves,† S.-T. Kim, M. A. Schmidt, P. M. Scola & S. L. Buchwald*
Org. Lett. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c05127)

The authors report a Cu-catalyzed method for the efficient coupling of base-sensitive aryl bromides and alcohols utilizing a newly developed N1,N2-diarylbenzene-1,2-diamine ligand. This ligand was developed to increase the Lewis acidity of the Cu center, thereby permitting the use of a substantially milder base (NaOTMS or NaOPh) relative to those required in a previous iteration of this methodology (NaOMe or NaOt-Bu). Under the optimized reaction conditions, several classes of previously incompatible aryl bromides were efficiently transformed, including base-sensitive heterocycles and those containing acidic functional groups.

Honourable highlights: Several standout papers narrowly missed a full write-up this week, due in part to email length constraints and to maintain a balanced mix of academic and industrial organic synthesis across the newsletter. Nevertheless, if you have a few extra minutes, the papers below are well worth your time.
The Catalytic Enantioselective [1,2]-Wittig Rearrangement Cascade of Allylic Ethers, M. N. Grayson, A. D. Smith and co-workers, Nat. Chem. 2026, DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02022-4.
Asymmetric C–H Functionalization of Bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes and Their 2-Oxa- and 2-Aza Derivatives via Rhodium Carbene Intermediates, D. G. Musaev & H. M. L. Davies and co-workers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c19070.
An Expedient Synthetic Route to the Long-Acting RSV Inhibitor JNJ-6231 via Stereoselective Enzymatic Amination and Regioselective Alkylation, K. Matcha and co-workers, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2026, DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.5c00352.
Cation Radical-Mediated Semi-Pinacol and n+2 Ring Expansions via Organic Photoredox Catalysis, D. A. Nicewicz and co-workers, Chem. Sci. 2026, DOI: 10.1039/D5SC08977H.

The U.S. Vaccine Rollback
💉 The U.S. Vaccine Rollback. If you have spent any time on social media lately, you will quickly encounter claims from anti-vaccine advocates—and echoed by President Trump—that U.S. children receive a staggering “72 vaccines”. That number is, of course, incorrect. It stems from a series of deliberate miscounts: it tallies doses rather than distinct vaccines and treats combination products as multiple separate shots. For example, a single MMR injection (measles, mumps, rubella) is often counted as three vaccines rather than one. In reality, the U.S. childhood schedule historically recommended about 17 distinct vaccines, translating to roughly 30 doses by age two that protect against about 15 diseases. Now, for the first time in decades, the CDC has narrowed the list of universally recommended childhood vaccines to 11, removing routine recommendations for hepatitis A and B, meningococcal disease, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, and COVID-19.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) argues that several vaccines lack evidence from “gold-standard” placebo-controlled trials. In fact, placebo-controlled trials are routinely conducted in early development when no effective vaccine exists, but once a vaccine’s safety and efficacy are proven, withholding it from a control group becomes unethical. At that stage, new vaccines are compared against existing standards of care rather than placebo. Demanding fresh placebo trials for rare but severe infections, such as meningococcal disease, would therefore be unethical as invasive meningococcal infections carry a 10–20% mortality rate, and roughly 20% of survivors suffer permanent complications (hearing loss, limb amputation, or neurological injury).
HHS has also pointed to Denmark’s smaller vaccine schedule as justification but Danish experts themselves caution against this comparison. Denmark benefits from lower disease incidence, universal health-care access, and near-complete prenatal screening—conditions that do not apply uniformly in the U.S. In more unequal health systems, broad vaccination plays a larger role in protecting children who might otherwise fall through the cracks.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply