- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- [3+3] Not [4+2]: A New Route to Six-Membered Rings
[3+3] Not [4+2]: A New Route to Six-Membered Rings
💡 Looking Back on 2025 and Forward into 2026

Note: This will be the final issue of the newsletter for 2025. We’ll be back on Monday 12th January 2026, when journals have resumed publishing as normal. Thank you all for reading and supporting the newsletter throughout 2025. Wishing those who celebrate a very happy Christmas, and all readers the best for the year ahead!
Monday 15th December – Sunday 21st December 2025 | Volume 2, Issue 48 |


Aziridine–Epoxide Heterocoupling: A Straightforward Approach to Stereoselective Synthesis of Complex Morpholine Derivatives
V. Murugesan, B. Hoot, W. Farris, P. Saini, A. I. Saucedo, S. Pradhan, T. Mitchell & C. P. Delaney*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c18227)
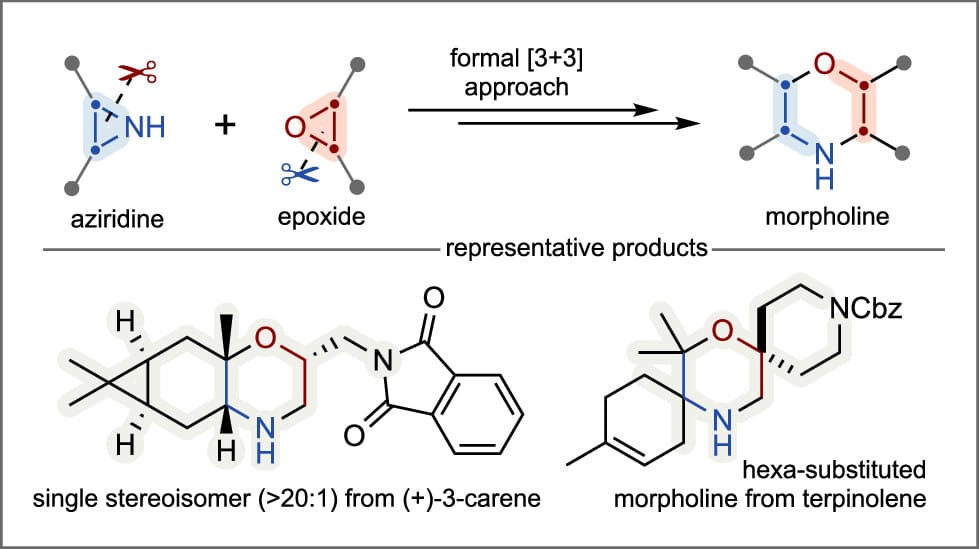
The authors report a general strategy for the annulative heterocoupling of aziridines and epoxides to synthesize highly substituted, N-unprotected morpholine derivatives via aziridinyl alcohols. Due to the accessibility of complex, stereodefined aziridines and epoxides, this approach allows for facile and combinatorial synthesis of substituted morpholine derivatives with handles for further elaboration, expanding access to densely substituted morpholine derivatives bearing multiple substituents.

Trifluoromethylation of Alkyl Electrophiles with 11C- or 18F-Labeled Fluoroform for PET Applications
C. Wang,† P. DeMent,† S. Jana, J. Hong, V. W. Pike* & W. Liu*
Science 2025, 390, 1278–1284 (DOI: 10.1126/science.ady2969)
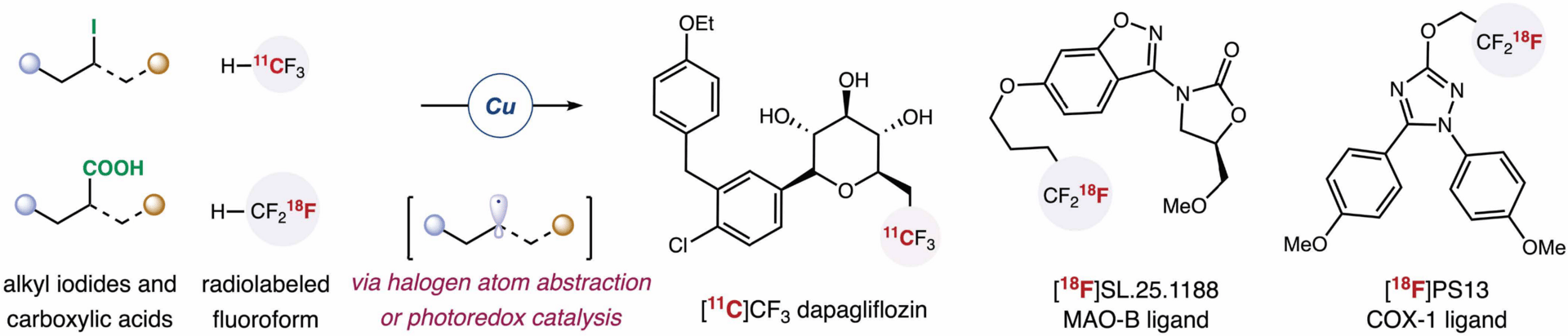
The authors present a general approach for late-stage installation of either a [18F]CF3 or [11C]CF3 group at a C(sp3) site. This method leverages unusual copper-mediated radiotrifluoromethylation of alkyl halides and alkyl carboxylic acids by halogen atom transfer and photoredox catalysis, respectively. More than 50 complex molecules and pharmaceutical agents were efficiently labeled with fluorine-18 (18F) or carbon-11 (11C).

Alkyl Sulfonyl Fluorides as Ambiphiles in the Stereoselective Palladium(II)-catalysed Cyclopropanation of Unactivated Alkenes
Y. Cao, W. Rodphon,‡ T. M. Alturaifi,‡ A. V. R. D. Lisboa, Z. Ren, J. J. C. Struijs, H.-Q. Ni, T. Savchuk, R. P. Loach, S. Yang, I. J. McAlpine, D. G. Blackmond, P. K. Mykhailiuk,* P. Liu,* K. B. Sharpless* & K. M. Engle*
Nat. Synth. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00925-1) 🔓
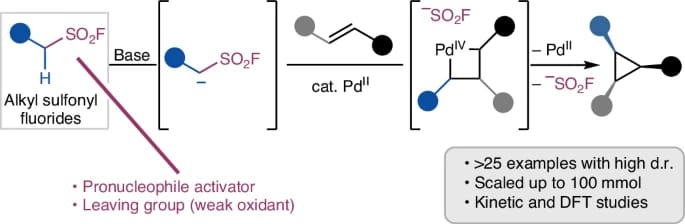
The authors present the ambiphilic reactivity of alkyl sulfonyl fluorides in the stereoselective synthesis of diverse cyclopropanes from olefins, under palladium(II) catalysis. The sulfonyl fluoride functionality serves as both an acidifying group and an internal oxidant within the ambiphile, enabling successive carbopalladation and oxidative addition steps in the catalytic cycle, respectively. The transformation accesses cis-substituted cyclopropanes and exhibits broad compatibility with various alkyl sulfonyl fluorides. With internal alkene substrates, 1,2,3-trisubstituted cyclopropanes that are otherwise challenging to synthesize are formed in good-to-moderate yields and predictable diastereoselectivity.
Divergent Synthesis of N Heterocycles from Carbocycles Enabled by Electrochemical Nitrogen Atom Insertion
G.-Q. Sun,† X. Wang,† R. Hu, W. Rao, Y. Zhao* & M. J. Koh*
Nat. Synth. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-025-00945-x)
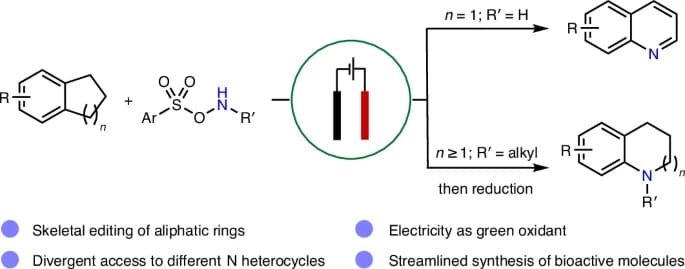
The authors report an electrochemical platform that enables efficient nitrogen atom insertion into saturated carbocycles under mild conditions. Two distinct protocols have been developed, allowing access to either functionalized quinolines or N-alkylated saturated N heterocycles, both with excellent selectivity and broad functional group tolerance. The synthetic utility of the approach is highlighted by the synthesis of two ion-channel antagonists.

Excited-State Configuration Controls the Ability of Nitroarenes to Act as Energy Transfer Catalysts
M. Rihtaršič,† B. Kweon,† P. T. Błyszczyk, A. Ruffoni, E. M. Arpa* & D. Leonori*
Nat. Catal. 2025 (DOI: 10.1038/s41929-025-01453-z) 🔓
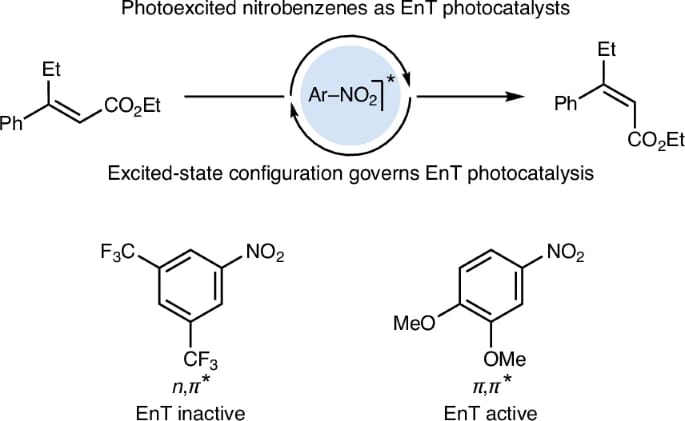
Energy transfer (EnT) catalysis allows selective triplet state population without singlet excitation, avoiding high-energy irradiation. Traditionally, this involves photosensitizers with matching triplet energies (ET) to substrates. Here, the authors propose using nitroarenes as photocatalysts, finding their efficiency depends on excited state localization rather than ET. Specifically, 3π,π* nitroarenes, with excitation on the aromatic core, outperform 3n,π* types. This concept is effective in contra-thermodynamic E-to-Z alkene isomerization and [2+2] cycloadditions. The energetic descriptor ΔETT is also introduced to differentiate 3n,π* and 3π,π* triplet states, aiding in identifying new photosensitizers.

A Divergent Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Coprophilin and Four Trichodermic Acids via a [1,5]-Hydride Shift–Aldol Cascade
E. Smith, T. C. Jenkins, C. S. Yeung & T. J. Donohoe*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c17359) 🔓
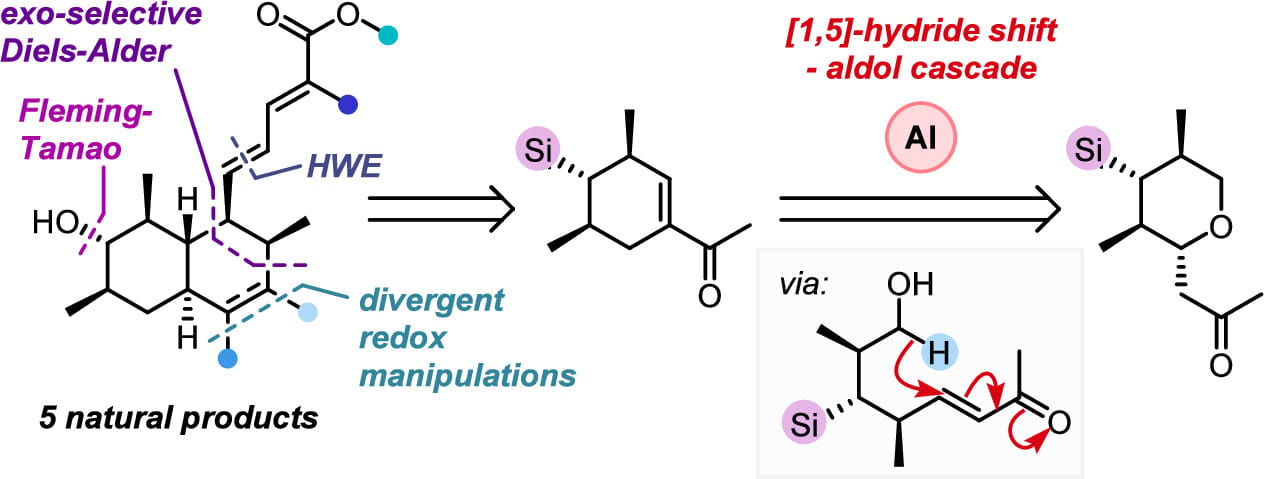
The asymmetric syntheses of coprophilin and four members of the trichodermic acid family of natural products are disclosed. This work employs several key transformations, including an aluminum-promoted [1,5]-hydride shift–aldol cascade reaction, an exo-selective Diels–Alder cycloaddition, and a late-stage Fleming–Tamao oxidation. These key steps efficiently construct the bicyclic core of the natural products, which can then be readily functionalized in a divergent manner, allowing the synthesis of a wide range of natural product targets.
Total Synthesis of Acoapetaludine A Enabled by a Rhodium-Catalyzed Domino Cyclization
Y. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Lei & Y. Jia*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c18189)
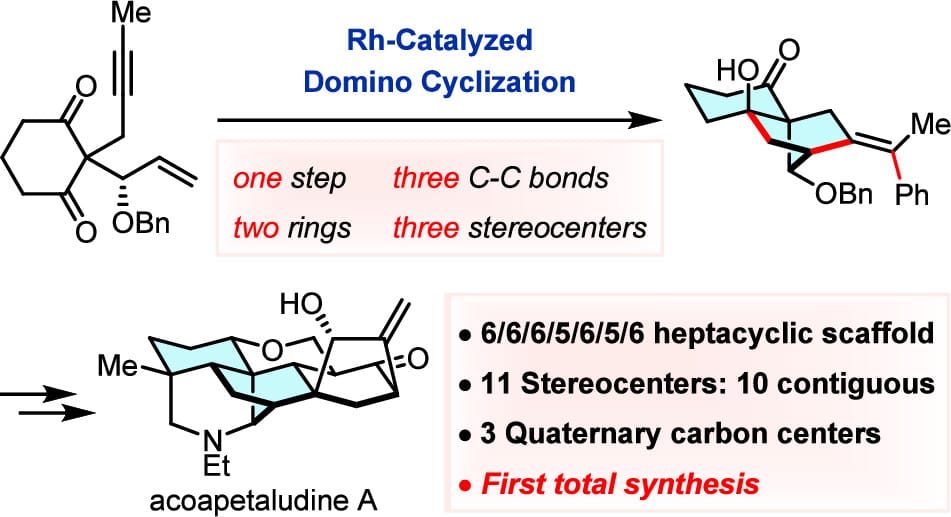
A rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric domino cyclization was developed, which enables the efficient assembly of highly strained bridged tricyclic scaffolds. Taken together with a deprotection/retro-aldol/intramolecular Mannich reaction cascade and a diastereocontrolled intramolecular Diels–Alder cycloaddition, the first total synthesis of C20-diterpenoid alkaloid acoapetaludine A has been achieved in a concise and practical manner.
Visible Light-Driven Contra-Thermodynamic Functional Group Transposition of Chalcones
C. Cruz,† J. Galicia,† S. Bowers, J. Hua & E. A. Romero*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c16361)

The authors report visible light-driven conditions to directly access transposed 1,2-diaryl enones from 1,3-diaryl enones (i.e. chalcones), creating a new contra-thermodynamic reactivity paradigm for this motif. The method is compatible with a range of functional group patterns and consistently delivers the products in excellent yields.
Evaluation of Elementary Steps in Csp2–Csp3 Cross-Electrophile Coupling Reactions Mediated by a Common Ni Complex
H. F. Starbuck, L. P. Dinh, D. Kalyani* & C. S. Sevov*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15344)
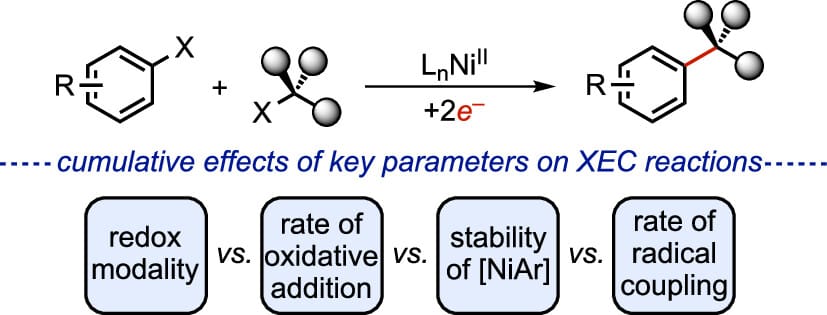
Cross-electrophile coupling (XEC) reactions are widely employed to rapidly construct C(sp2)–C(sp3) bonds from available substrates. Key elementary steps of the reaction, such as oxidative addition and radical coupling, have been individually investigated with discrete complexes, but no studies exist that probe these and other key steps along the reaction pathway from a single, synthetically relevant platform. This work leverages the accessibility of persistent organonickel complexes to benchmark the effects of electronic and steric parameters of complexes and substrates on the rates of oxidative addition, the stabilities of organonickel intermediates, and the rates of radical coupling.
Air-Stable Tetrazene Radical Cation Salts: Structural Requirements and Oxidation Catalysts
A. Oshiro, Y. Sasano,* S. Saito, Y. Araki, S. Sugiyama, E. Kwon, S. Kajimoto, Y. Kuriyama, S. Yoshinaga, M. Takahashi, K. Sato, N. Shida, Y. Ishigaki, M. Atobe & Y. Iwabuchi*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15272) 🔓

In this study, stable tetrazene radical cation salts were synthesized and characterized for the first time. The radical cation derived from 1,2-di(2-azaadamantan-2-yl)diazene (DAD) was isolated as an air-stable solid, retaining its integrity for at least 120 days at ambient temperature (∼25 °C) and pressure. X-ray crystallography and electron spin-resonance spectroscopy revealed the delocalization of the unpaired electron over the tetrazene core and into the adamantane framework. DAD undergoes two well-separated, reversible redox processes and displays high catalytic activity for alcohol oxidation under mild conditions.

Engaging Tertiary Benzylic Radicals in Metallaphotoredox Catalysis: A Modular Approach to Access Diaryl Quaternary Centers
S. L. Goldschmid, H. L. Hutchinson, T. C. Sherwood, C. L. Joe, E. R. Welin & T. Rovis*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202521490)

The authors report the decarboxylative cross-coupling of tertiary benzylic carboxylic acids and aryl bromides to furnish all-carbon diaryl quaternary centers. For the first time, tertiary benzylic radicals are introduced as viable participants in metallaphotoredox-catalyzed cross-couplings by suppressing undesired benzylic radical dimerization via fast radical trapping with Cu. The functionalization of feedstock carboxylic acids as well as late-stage functionalization of carboxylic acid-containing drugs is demonstrated.
Asymmetric Hydride Shift Reactions Catalyzed by Chiral Aluminium Complexes
M. M. Amer,† J. Hou,† J. Wang, A. Mazeikaite & T. J. Donohoe*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, Early View (DOI: 10.1002/anie.202521374) 🔓
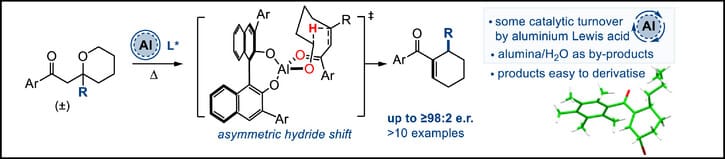
An asymmetric intramolecular hydride shift reaction has been developed that is catalyzed by Al Lewis acids in conjunction with a chiral BINOL-derived ligand. Racemic THP substrates are transformed into cyclohexene products via a prochiral intermediate ring opened enone; which then undergoes a key 1,5-hydride shift reaction. This reaction is operationally simple, works well on a gram scale, and the desired products are formed with high enantioselectivity (up to >98:2 e.r.).

Machine Learning-Guided Photocatalytic Cross-Coupling of Phenols and Heteroaryl Halides
M. C. Carson, A. Wu, K. B. Duggal, M. E. Rotella & M. C. Kozlowski*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-5vcsz) 🔓

The authors report a photochemical strategy that couples phenols with heteroaryl halides under redox-neutral conditions using an organic dye photocatalyst and base. Concurrent oxidation of the phenol component and reduction of the azine component generates complementary radicals that cross-couple efficiently, delivering moderate to high yields (up to 91%) with high functional group tolerance. Mechanistic experiments and DFT studies elucidate the radical reaction pathways, while substrate clustering, HTE, and ML enable prediction of C–C versus SNAr reactivity across broad chemical space.
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Two Aromatized Halicyclamines
Z. D. Firestone, T. A. Grigolo, F. G. Pernichelle & J. M. Smith*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-m9ksj) 🔓

The concise and divergent syntheses of the marine alkaloids (+)-tetradehydrohalicyclamine B and (–)-epi-tetradehydrohalicyclamine B are disclosed. Each synthesis requires ten steps and hinge on several key transformations including an enantioselective organocatalyzed Michael addition, a macrocyclic aza-Wittig ligation, and reagent-controlled stereodivergent lactam reductions to assemble their core molecular frameworks.
Geminal Difunctionalization of Ketones via C–S Bond Insertion of Photogenerated Donor–Donor Diazo Compounds
V. George, A. Pattanaik, D. Maddox, L. M. Sigmund, G. Mejia, S. Pahlén, S. Angerer, M. Schmoll, L. M. Schneider, N. Selmi, M. Kabeshov, G. Bergonzini, J. Rehbein & B. König*
ChemRxiv 2025 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-j6p2h) 🔓
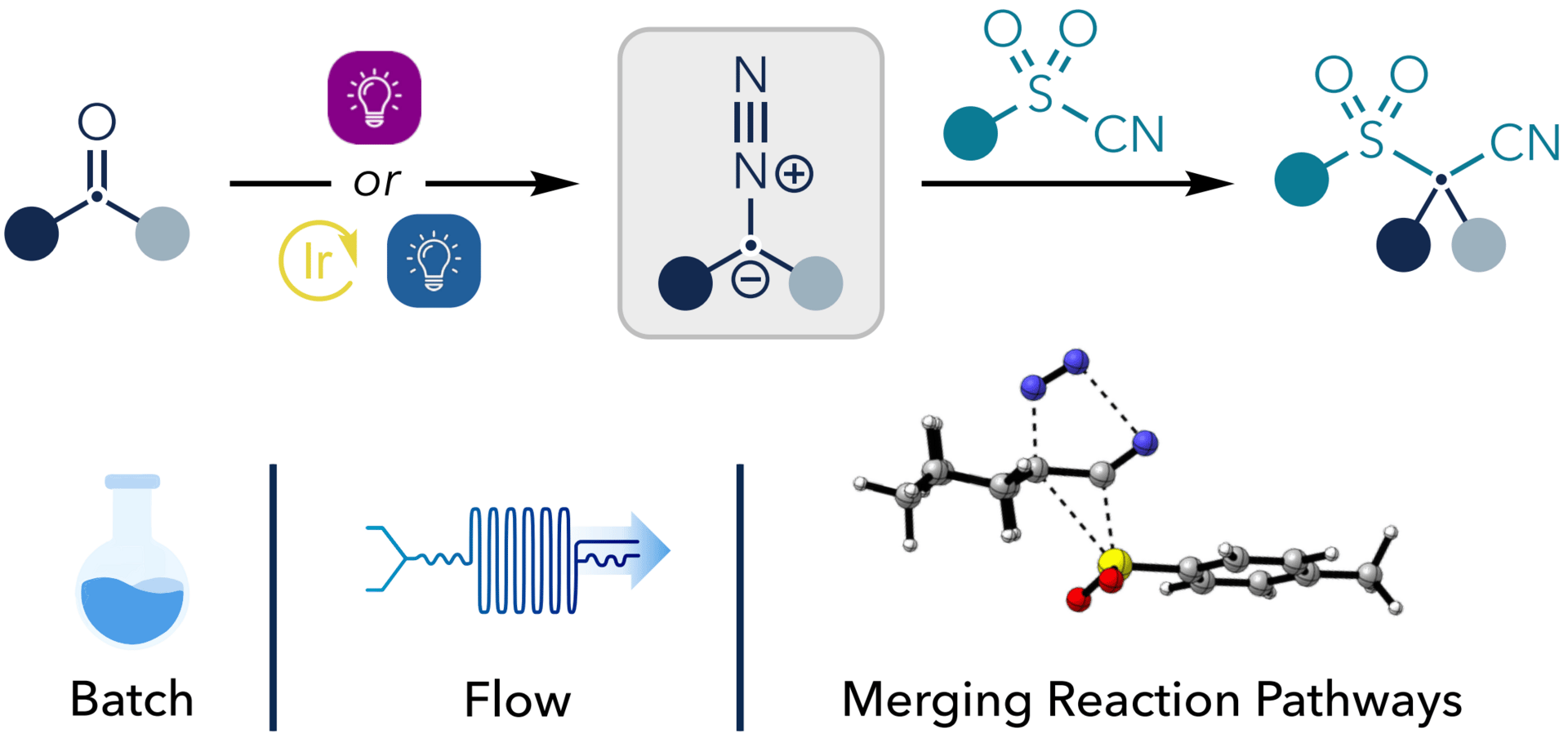
The authors report a metal-free migratory insertion of diazo compounds into carbon–sulfur bonds of sulfonyl cyanides, enabling the simultaneous installation of sulfone and nitrile functionalities at a single carbon center. In this strategy, inherently unstable diazo intermediates are generated in situ via photochemical decomposition of bench-stable oxadiazolines, which are readily synthesized from the corresponding ketones. The reaction exhibits broad functional group, water, and air tolerance, and affords high yields with excellent diastereoselectivity in constrained cyclic systems.

Synthesis of Heterobicyclo[n.1.1]alkanes
R. I. Revie,† J. Ragus† & E. A. Anderson*
Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, Review Article (DOI: 10.1039/D5CS01128K) 🔓

Heterocyclic bicyclo[n.1.1]alkanes have emerged as important scaffolds in contemporary drug design due to their rigid frameworks that enable the positioning of their subsituents along well defined vectors in chemical space. Offering much potential as alternative cores to traditional benzene rings, heterobicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes (HBCHexs) and heterobicyclo[3.1.1]heptanes (HBCHeps) in particular have attracted significant attention from the synthetic community. A plethora of methods have recently been developed to access these useful motifs, using both radical and polar strategies to forge the bicyclic system. This review discusses recent developments in the field, with a focus on mechanistic aspects, and those methodologies that show the most potential for general application.

2025 → 2026
✍️ 2025 → 2026. 2025 was not an easy year for science. In the United States in particular, political disruption created funding uncertainty, weakened public-health policy, and left many researchers questioning the stability and safety of their careers. Despite this, scientific progress continued, and Nature have highlighted several positive developments from 2025 that point toward a more hopeful 2026:
Gene editing reached major clinical milestones, including the first gene therapy for Huntington’s disease, which slowed cognitive decline in participants by 75%.
Conservation efforts delivered measurable results, with several species removed from high-risk categories. Notably, the green sea turtle—endangered since the 1980s—was reclassified as being of least concern.
Clean energy passed a global tipping point, with renewables overtaking coal as the world’s largest source of electricity for the first time, driven largely by rapid solar and wind deployment in China.
Public-health response capacity improved, as an Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo was contained in just over a month through rapid diagnostics, vaccination, and local coordination.
Looking ahead, Nature also reported several scientific developments to watch in 2026:
Artificial intelligence will become more deeply embedded in research, with AI systems increasingly designing experiments, analysing data, and coordinating complex workflows. The primary challenge will shift from capability to governance, ensuring reliability, transparency, and accountability as human oversight decreases.
Clinical research may accelerate, driven by regulatory reforms in the UK and proposed changes in the United States aimed at simplifying trial approval. A UK trial of a single blood test designed to detect around 50 cancers before symptoms arise is also expected to report results next year.
Personalised gene-editing trials are expected to scale-up, particularly for rare metabolic disorders, building on the clinical successes seen in 2025.
If 2025 demonstrated anything, it is that scientific progress is increasingly global—distributed across countries, disciplines and institutions—and despite political upheaval, science continues to move forward through evidence and collaboration.
Thank you for reading Synthesis Spotlight this year!
That’s all for this issue. Have a great Christmas and New Year! We’ll see you next year on Monday 12th January 2026.

Reply