- Synthesis Spotlight
- Posts
- 1. Couple, 2. Close
1. Couple, 2. Close
💡 Trump vs. Science: A Year of Cuts, Freezes, and Uncertainty

Monday 19th January – Sunday 25th January 2026 | Volume 3, Issue 3 |


Couple-Close: Unified Approach to Semisaturated Cyclic Scaffolds
J. Xie, W. Y. Zhao, J. Z. Wang, W. L. Lyon, N. Takanashi, A. Long, T. M. Sodano, C. B. Kelly, M. C. Bryan & D. W. C. MacMillan*
Science 2026, 391, 399–406 (DOI: 10.1126/science.aec5748)

Semisaturated cyclic scaffolds, whose specific blend of Csp2- and Csp3-hybridized components confers distinct properties, are increasingly sought after. However, existing methods to construct these scaffolds are limited, often relying on arene saturation or annulations that require lengthy de novo syntheses. Here, the authors describe a unified and highly modular couple-close strategy for the synthesis of semisaturated scaffolds. Bifunctional linkers are installed onto aromatic rings through diverse bond-forming reactions, and subsequent cyclization furnishes semisaturated bicyclic adducts via a mechanistically distinct cobalt-catalyzed dehydrogenative radical cyclization that is effective even on electronically unbiased arenes.

Collective Intelligence for AI-Assisted Chemical Synthesis
H. Li,† S. Sarkar,† W. Lu, P. O. Loftus, T. Qiu, Y. Shee, A. E. Cuomo, J.-P. Webster, H. R. Kelly, V. Manee, S. Sreekumar, F. G. Buono, R. H. Crabtree, T. R. Newhouse* & V. S. Batista*
Nature 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-026-10131-4)
Previously: ChemRxiv (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv-2025-dc28b) 🔓
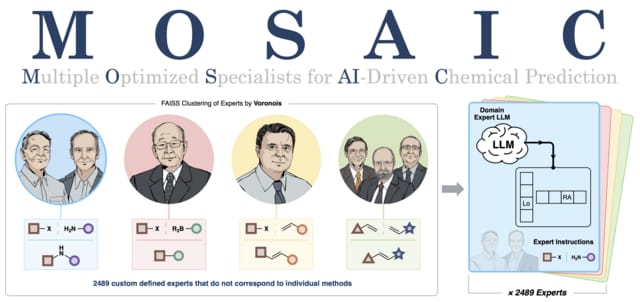
The authors introduce MOSAIC (Multiple Optimized Specialists for AI-assisted Chemical Prediction), a computational framework that enables chemists to harness the collective knowledge of millions of reaction protocols. MOSAIC is built upon the Llama-3.1-8B-instruct architecture, training 2,498 specialized chemical experts within Voronoi-clustered spaces. This approach delivers reproducible and executable experimental protocols with confidence metrics for complex syntheses. With an overall 71% success rate, experimental validation demonstrates the realizations of over 35 novel compounds, spanning pharmaceuticals, materials, agrochemicals, and cosmetics. Notably, MOSAIC also enables the discovery of new reaction methodologies that are absent from the expert’s training, a cornerstone for advancing chemical synthesis.

Hyperpyramidalized Alkenes with Bond Orders Near 1.5 as Synthetic Building Blocks
J. Ding,† S. A. French,† C. A. Rivera, A. T. Meza, D. C. Witkowski, K. N. Houk & N. K. Garg*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02055-9) 🔓

Alkenes typically have trigonal planar geometries at each terminus, with favourable σ- and π-bonding leading to a bond order of ~2. Here, the authors consider unusual alkenes that possess an extreme form of geometric distortion, termed hyperpyramidalization. In a hyperpyramidalized alkene, geometries deviate remarkably from the typical trigonal planar alkene geometry, leading to weak π-bonding and abnormal alkene bond orders approaching 1.5. Cubene and 1,7-quadricyclene, first validated in 1988 and 1979, respectively, are the focus of the present study, and their unusually weak π-bonds have been leveraged in cycloadditions, enabling the construction of complex scaffolds and access to previously unrealized chemical space.
Collective Asymmetric Synthesis of the Strychnos Alkaloids via Thiophene S,S-Dioxide Cycloadditions
K. H. Park,† J. Park,† N. Frank, H. Zhang, P. Tian, Y. Biddick, F. Duarte* & E. A. Anderson*
Nat. Chem. 2026 (DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02041-1) 🔓

The authors report that thiophene S,S-dioxides (TDOs) offer a modular, rapid entry to Strychnos natural products via inverse electron demand Diels–Alder cascades. Exceptional levels of stereocontrol were achieved in asymmetric TDO cycloadditions, affording tricyclic indolines of utility in medicinal chemistry research and enabling the stereoselective synthesis of eight Strychnos alkaloids by the shortest routes described so far, including a synthesis of the iconic family member brucine.

A Diazo-free Equivalent of the Unsubstituted Carbyne Cation: Straightforward Synthesis of Naphthalenes and Pyridines via [12/13CH]+ Insertion
N. S. Wenzel,† P. C. Brehm,† M. Mücke, M. A. Ansari, B. Worbs, M. Simon, C. Golz, R. A. Mata & M. Alcarazo*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c21901) 🔓

Stable isotope labeling is crucial in pharmaceutical research to understand the mode of action and metabolism of new drug candidates; however, its utility is often jeopardized by the synthetic challenges associated with installation of the isotopic label. Here, the authors address this problem for the case of 13C-labeled naphthalene and pyridine building blocks. The synthetic protocol utilizes a sulfonium sulfaneylidene salt, a benchtop stable reagent that does not incorporate diazo functionalities in its structure; yet, under Rh-catalysis, it efficiently acts as a synthetic equivalent of the simplest conceivable carbynyl cation, the [CH]+ fragment.
16-Step Scalable Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Tetrodotoxin
C. Peng, W. Wu, Y. Ye* & P. Hu*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c20700)

Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin and a promising analgesic that selectively blocks voltage-gated sodium channels at nanomolar concentrations. Its complex structure features an octa-substituted cyclohexane core, excessive polar functionalities, and exceedingly high (1:1) heteroatom-to-carbon ratio. Prior syntheses required 22–69 steps from heavily oxygenated starting materials, with excessive protecting group and functional group manipulations. Here, the authors report a scalable 16-step synthesis from simple para-bromobenzyl alcohol via a distinct chemoenzymatic strategy.
Catalytic Stereospecific Construction of Aminocyclopropanes from β-Boryl Amides
X. Zhang,† L. Cheng,† M. Chapman† & J. P. Morken*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c21144)
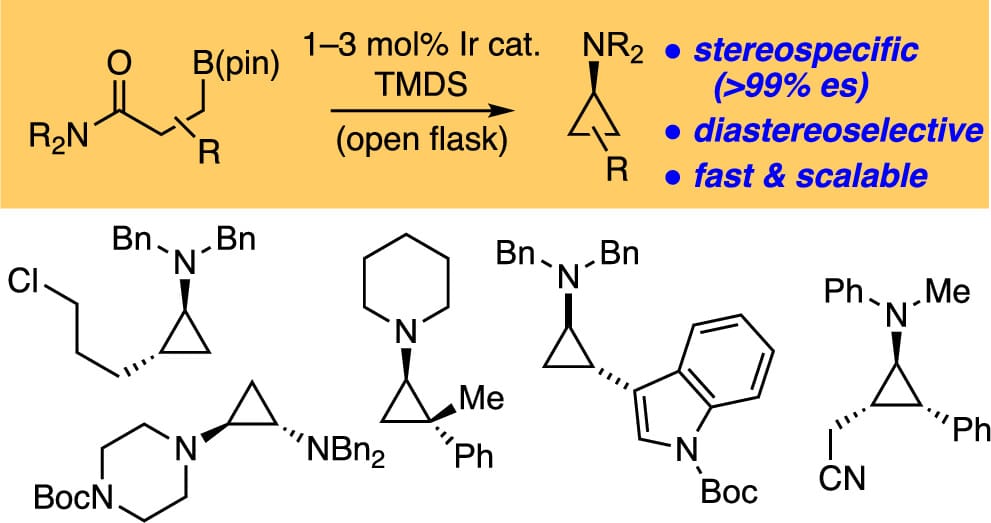
Iridium-catalyzed reduction of β-boryl amides with tetramethyldisiloxane affords iminium ions in situ. These reactive iminium ions are directly trapped by stereospecific (invertive) reaction with the boronate, delivering aminocyclopropanes (ACPs) in excellent yield, diastereoselectivity, and enantiospecificity. The reaction applies to both secondary and tertiary benzylic boronates, allylic boronates, and α-substituted boronates, giving access to many multiply substituted ACPs.
Iridium-Catalyzed Stereoselective α-Alkylation of α-Hydroxy Ketones with Minimally Polarized Alkenes
Y. Wang, F. Hong, C. M. Robertson, R. J. Mudd & J. F. Bower*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c19724) 🔓
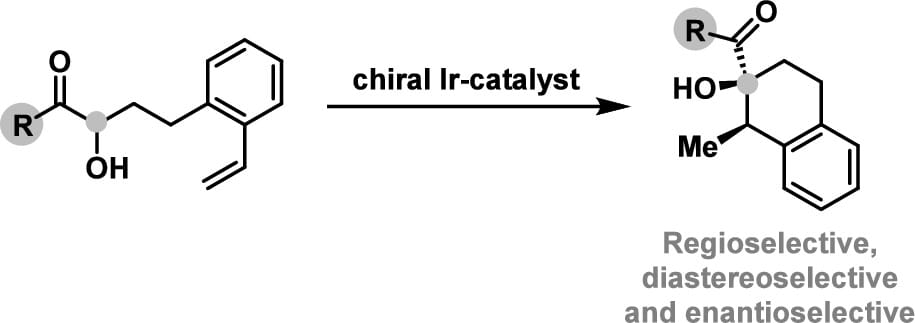
Cationic Ir(I)-complexes modified with homochiral diphosphines promote the α-C-H addition of α-hydroxy ketones to styrenes or alkyl olefins. These processes are predicated on the hydroxyl-directed formation of an Ir-enolate. Inter- and intramolecular processes are feasible, with the latter offering stereocontrolled access to carbocycles bearing two new stereocenters. The intramolecular processes constitute rare examples of alkene-based Conia-ene reactions that are enantio- and diastereoselective.

Utilizing 1,4-Dihydropyridines for C–N Bond Activation: A Photoredox-Catalyzed Deaminative Approach toward Benzylic Quaternary Carbon Centers
H. L. Hutchinson, S. L. Goldschmid, T. C. Sherwood, C. L. Joe, E. R. Welin & T. Rovis*
ACS Catal. 2025, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.5c07931)

The authors report the C–N bond cleavage of 1,4-dihydropyridines, a substrate class readily synthesized from primary amines, to generate tertiary benzylic radicals for selective radical trapping. Using photoredox catalysis, this method serves as a valuable strategy for constructing quaternary carbon centers. Scope studies reveal broad tolerance of primary amines with electron-neutral, electron-rich, and electron-withdrawing substituents on the benzylic moieties. Finally, the comparison of this method to other deaminative methods further illuminates the substrate tolerance and mechanistic nuances between amine activation platforms.

Stereoretentive Radical-Radical Cross-Coupling
Y. Wang, J. Sun, Y. Li, D. A. Cagan, O. T. Ring, X. Zeng, J. Tsien, L. Massaro, J. E. Smith, B. J. Orzolek, M. R. Collins, Y. Kawamata & P. S. Baran*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10001512/v2) 🔓

The authors report the first stereoretentive radical-radical cross-coupling of two distinct unstabilized alkyl radicals derived from enantioenriched sulfonylhydrazides and achiral alkyl halides without chiral catalysts, directing groups, or exogenous redox. This substrate-controlled approach leverages a nickel-catalyzed, redox-neutral manifold, enabling precise kinetic matching of diazene-mediated radical generation and halogen atom transfer. Optimization via high-throughput experimentation yields products with excellent enantiospecificity (typically 80–96% e.s.) and synthetically useful yields (40–90%) across diverse piperidine and pyrrolidine scaffolds with remarkable chemoselectivity, tolerating ethers, free amines, aryl halides, heterocycles, olefins, and other sensitive motifs. Synthetic utility is demonstrated through streamlined access to medicinally relevant intermediates and natural products like (S,S)-stenusine.
Total Synthesis of Allocyclinone A via Late-Stage Halogen Swapping
T.-H. Chao, E. B. Barrois, C. W. Johnston & H. Renata*
ChemRxiv 2026 (DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.10001470/v1) 🔓
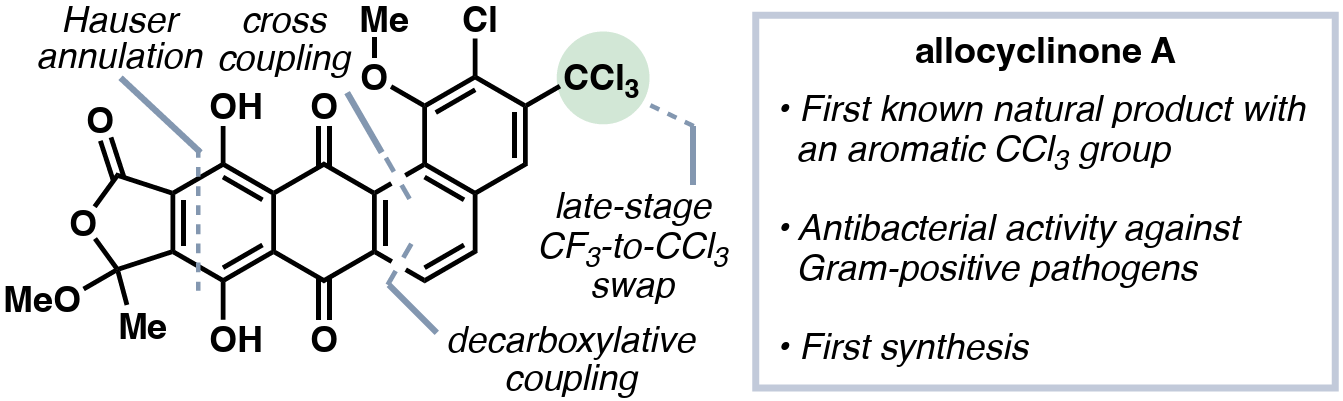
The authors describe the total synthesis of allocyclinone A, an angucyclinone antibiotic with an unprecedented aromatic trichloromethyl motif. While attempts to effect late-stage enzymatic halogenation with the native halogenases from allocyclinone biosynthesis were unsuccessful, a late-stage halogen swap to convert an aromatic trifluoromethyl to its trichloromethyl counterpart proved facile, affording the first synthesis of the natural product.

Stereodefined Synthesis of 3-Difluoromethyl-Benzoxaboroles: Novel Antimicrobials with Unlocked H-Bonding
A. Dimasi, A. Montoli, C. Lutti, A. Citarella, P. Ronchi, F. Castagnini, V. Mileo, G. Macetti, V. Baldelli, E. Rossi, P. Landini, D. Passarella & V. Fasano*
Org. Lett. 2026, ASAP (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c04602) 🔓

Benzoxaboroles, prominent scaffolds in medicinal chemistry, are typically modified on the benzene ring. In contrast, functionalization of the oxaborol ring is less common and often challenging. Indeed, 3-hydroxy-benzoxaboroles are virtually impossible to isolate due to their tautomeric equilibrium with the carbonyl form. In this work, the authors introduce a novel class of stereodefined 3-difluoromethyl-benzoxaboroles. The replacement of the hydroxy group with −CHF2 preserves stability while promoting bioactivity, owing to the lipophilic H-bond donor properties of the latter.

Trump vs. Science
🥊 Trump vs. Science. More than 7,800 research grants were cancelled or frozen in 2025, around 25,000 staff left federal agencies, and the White House proposed cuts of 35% ($32 billion) to non-defence research and development. Since January 2025, the Trump administration has moved rapidly to curtail federally supported research. A recent Nature feature documents the scale of this disruption and the speed with which it has unfolded.
At the centre of the cuts were unprecedented grant terminations with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) cancelling or suspending 5,844 grants, and the National Science Foundation (NSF) 1,996—disproportionately affecting research on infectious diseases, vaccines, and public health. Although courts have ordered the reinstatement of thousands of awards, roughly 2,600 grants, worth an estimated $1.4 billion, remain unfunded. New funding has also slowed: last year, the NSF issued 25% fewer grants than its ten-year average, while the NIH funded 24% fewer.
The contraction extends to the workforce with federal science agencies, including the EPA, NASA, and FDA, losing roughly 20% of staff in 2025, with more than 25,000 scientists and support personnel departing through layoffs or incentive-based resignations, placing further strain on remaining staff. Early-career pipelines are also narrowing with new international student enrolment falling 17% in 2025–26, and postdoctoral and tenure-track openings declining in chemistry, biomedical engineering, and ecology.
Legal challenges have rolled back parts of the early disruption, Congress has resisted the most severe cuts, and final budgets remain unsettled. US science retains a resilient and highly skilled workforce, but the central question is how quickly stability can be restored.
That’s all for this issue! Have a great week and we’ll see you next Monday.

Reply